MicroRNA-221/222 Inhibits the Radiation-Induced Invasiveness and Promotes the Radiosensitivity of Malignant Meningioma Cells
- PMID: 32983973
- PMCID: PMC7477324
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01441
MicroRNA-221/222 Inhibits the Radiation-Induced Invasiveness and Promotes the Radiosensitivity of Malignant Meningioma Cells
Abstract
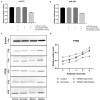
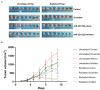
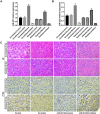
The controversy of adjuvant radiotherapy of meningiomas is at least partially due to the insufficient understanding on meningioma cells' response to irradiation and the shortage of radiosensitivity-promotion methods. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 were identified as critical regulators of radiosensitivity in several other tumors. However, their effect in meningiomas has yet to be confirmed. Therefore, the malignant meningioma IOMM-Lee cells were adopted, transfected with microRNA-221/222 mimics or inhibitors, and irradiated with different dosages. The effects of radiation and microRNA-221/222 were then assessed in vitro and in vivo. Radiation dose increases and microRNA-221/222 downregulation synergistically inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation, prevented xenograft tumor progression, and promoted apoptosis, but antagonistically regulated cell invasiveness. Pairwise comparisons revealed that only high-dose radiations (6 and 8 Gy) can significantly promote cell invasiveness in comparison with unirradiated counterparts. Further comparisons exhibited that downregulating the microRNA-221/222 expression can reverse this radiation-induced cell invasiveness to a level of untransfected and unirradiated cells only if cells were irradiated with no more than 6 Gy. In addition, this approach can promote IOMM-Lee's radiosensitivity. Meanwhile, we also detected that the dose rate of irradiation affects cell cycle distribution and cell apoptosis of IOMM-Lee. A high dose rate irradiation induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis-promoting effect. Therefore, for malignant meningiomas, high-dose irradiation can facilitate cell invasiveness significantly. Downregulating the microRNA-221/222 level can reverse the radiation-induced cell invasiveness while enhancing the apoptosis-promoting and proliferation-inhibiting effects of radiation and promoting cell radiosensitivity.
Keywords: IOMM-Lee; dose rate; epithelial–mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors; invasiveness; microRNA-221/222; radiosensitivity.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Song, Huo, Wang, Zhang, Hao, Jia, Kong, Jia, Wu, Xu, Jia and Zhang.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RAS Promotes Proliferation and Resistances to Apoptosis in Meningioma.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):779-787. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9763-z. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27021020
-
Alpha-synuclein contributes to malignant progression of human meningioma via the Akt/mTOR pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Nov 15;16:86. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0361-y. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 27895530 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro assessment of radiobiology of meningioma: A pilot study.J Neurosci Methods. 2019 Jan 1;311:288-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 5. J Neurosci Methods. 2019. PMID: 30408557
-
Calcium channel antagonists augment hydroxyurea- and ru486-induced inhibition of meningioma growth in vivo and in vitro.Neurosurgery. 2006 Nov;59(5):1109-20; discussion 1120-1. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000245597.46581.FB. Neurosurgery. 2006. PMID: 17143245
-
Celecoxib inhibits meningioma tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model.Cancer. 2007 Feb 1;109(3):588-97. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22441. Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17177201
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs as Genetic Biomarkers for the Diagnosis, Prognosis, Radiosensitivity, and Histopathologic Grade of Meningioma.Cureus. 2023 Feb 3;15(2):e34593. doi: 10.7759/cureus.34593. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36883085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNA landscape and their emerging roles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in meningioma.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Feb 27;32(1):200782. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200782. eCollection 2024 Mar 21. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38596289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of publication trends in meningioma research (1992 - 2023).Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Aug 8;48(1):595. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03739-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40779080 Review.
-
LncRNA-IMAT1 Promotes Invasion of Meningiomas by Suppressing KLF4/hsa-miR22-3p/Snai1 Pathway.Mol Cells. 2022 Jun 30;45(6):388-402. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.2232. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 35680373 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant Progression Contributes to the Failure of Combination Therapy for Atypical Meningiomas.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 15;10:608175. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.608175. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33520718 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

