Clinical Correlation of Wnt2 and COL8A1 With Colon Adenocarcinoma Prognosis
- PMID: 32983993
- PMCID: PMC7484937
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01504
Clinical Correlation of Wnt2 and COL8A1 With Colon Adenocarcinoma Prognosis
Abstract
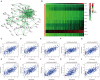
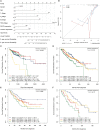
Wnt2 mRNA is widely expressed in various tumor tissues. Wnt2 overexpression promotes tumor growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis. However, its underlying molecular action mechanisms and clinical implications in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) remain unclear. mRNA expression data, obtained from tissue samples, and pathophysiological data of 368 COAD patients were obtained from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Further, Pearson's correlation analysis was performed to explore the correlation between the expression levels of Wnt2 and other genes in the human genome. Subsequently, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed for hub gene identification. Overall survival and significance were determined by Kaplan-Meier analysis, and the log-rank test was used to further identify genes with prognostic significance in COAD from GEO datasets (GSE17538 and GSE39582). Subsequently, 158 tissue samples from Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University were used for expression verification. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed on high and low Wnt2 expression datasets to identify potential signaling pathways activated in COAD. In all, 10 hub genes associated with Wnt2 were screened by Pearson's correlation analysis and PPI network, with Wnt2 and COL8A1 having significantly poor prognosis by Kaplan-Meier analysis and log-rank test. Furthermore, high expressions of COL8A1 and Wnt2 were associated with poor survival both in TCGA and GEO cohorts. We further found a correlation between the expressions of Wnt2 and COL8A1 in COAD as per immunohistochemical analysis. To further elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms of Wnt2 in COAD, we searched for pathways enriched in Wnt2 overexpressing datasets by GSEA. Our findings revealed that high Wnt2 levels were significantly associated with extracellular matrix receptor and focal adhesion pathways. Wnt2 expression correlated with COL8A1 expression in COAD; patients with high Wnt2 and COL8A1 expressions had worse survival outcomes. Pathways identified in this study prompt the molecular role of Wnt2 in COAD and provide directions to further elucidate the involved molecular mechanisms in COAD.
Keywords: Wnt2; bioinformatics analysis; collagen type VIII alpha 1 chain; colon adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Jiang, Li, Fan, Li, Jin, Li, Jin, Zhang, Mao and Hua.
Figures



References
-
- Katoh M. WNT2 and human gastrointestinal cancer (review). Int J Mol Med. (2003) 12:811–6. - PubMed
-
- Huguet EL, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Bicknell R, Harris AL. Differential expression of human Genes 2, 3, 4, and 7B in human breast cell lines and normal and disease states of human breast tissue. Cancer Res. (1994) 54:2615–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

