miR-452 Reverses Abnormal Glycosylation Modification of ERα and Estrogen Resistance in TNBC (Triple-Negative Breast Cancer) Through Targeting UGT1A1
- PMID: 32983995
- PMCID: PMC7479224
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01509
miR-452 Reverses Abnormal Glycosylation Modification of ERα and Estrogen Resistance in TNBC (Triple-Negative Breast Cancer) Through Targeting UGT1A1
Abstract
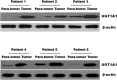
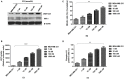
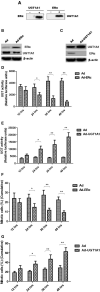
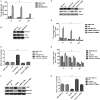
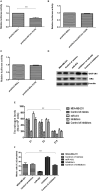
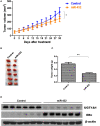
Background: The breast epithelial cells in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) actually have specific estrogen receptor (ER) expression, and the abnormal glycosylation of UGT1A1 in TNBC cells resulted in abnormal expression and function of ERα through regulating the modification of ERα. Therefore, our study targets the role of UGT1A1 expression, then glycosylation modification of ERα (estrogen receptor α) and estrogen resistance in development of TNBC. Methods: The differential expression of mRNA and miRNA in TNBC tissues was tested. Luciferase activity was analyzed in TNBC cells treated with miR-452. Moreover, the human mammary gland and TNBC cell lines were dealt with estrogen and miR-452 or its inhibitors, then proliferation ability was further determined. Moreover, the role of interaction between UGT1A1 and ERα in the glycosylation modification of ERα and UGT activity, and metabolism of estrogen were assessed. The effects of miR-452 on TNBC by improving abnormal glycosylation modification of ERα by targeting UGT1A1 and estrogen resistance were studied in vitro and in vivo. Results: The expression level of UGT1A1 in TNBC tumor tissues was higher than its matched para-tumorous tissues, but the miR-452 expression was opposite. The glycosylation modification site of ERα expressed in TNBC cells was different from that of normal mammary epithelial cells. The estrogen 17β-estradiol (E2) significantly promoted mitotic entry of TNBC cells. The interaction between UGT1A1 and ERα affected the expression level of each other, as well as the UGT enzyme activity and proliferation of TNBC cells. UGT1A1 induced production of intracellular estrogens and TNBC proliferation, but it could be reversed by overexpression of ERα. Upregulation of ERα caused the downregulation of UGT1A1 and marked decrease of intracellular estrogen products, and then suppressed TNBC proliferation. Moreover, UGT1A1 was the target gene of miR-452; miR-452 antagomir restrained TNBC xenograft. Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that estrogen was a positive factor in the proliferation of TNBC cells at onset of mitosis through accentuating the expression and enzyme activity of UGT1A1. However, miR-452 targeted to UGT1A1, then regulated glycosylation modification of ERα, estrogen metabolism, and TNBC development associated with estrogen resistance.
Keywords: UGT); estrogen receptor (ER); estrogen resistance; glycosylation modification; triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC); uridine diphosphate glucuronyl transferase (UDPGT.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Zhou, Mao, Shen, Zhao, Xu, Lin, Zhang, Cao, Xu, Chen, Zhang and Sun.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Advances in drug resistance of triple negative breast cancer caused by pregnane X receptor.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep 24;14(9):335-342. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i9.335. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37771631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The vitamin D analog EB1089 sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to the antiproliferative effects of antiestrogens.Adv Med Sci. 2024 Sep;69(2):398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2024.08.004. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Adv Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39233278
-
Estrogen regulates miRNA expression: implication of estrogen receptor and miR-124/AKT2 in tumor growth and angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36940-36955. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9230. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27175587 Free PMC article.
-
WBP2 Downregulation Inhibits Proliferation by Blocking YAP Transcription and the EGFR/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):1968-1982. doi: 10.1159/000492520. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30092563
-
Current progress and prospects for G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in triple-negative breast cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 27;12:1338448. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1338448. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38476263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concanavalin A inhibits human liver cancer cell migration by regulating F-actin redistribution and assembly via MAPK signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2022 Sep 23;24(5):405. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13525. eCollection 2022 Nov. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36276493 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of estrogen receptor α in endometrial carcinoma (Review).Oncol Lett. 2023 Oct 25;26(6):530. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14117. eCollection 2023 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38020303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in drug resistance of triple negative breast cancer caused by pregnane X receptor.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep 24;14(9):335-342. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i9.335. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37771631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01140 Targeting miR-452-5p/RGS2 Pathway to Attenuate Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis.Dis Markers. 2022 Oct 17;2022:2434938. doi: 10.1155/2022/2434938. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36299824 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-452: a double-edged sword in multiple human cancers.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 May;25(5):1189-1206. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-03041-0. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36622551 Review.
References
-
- Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU, Polyak K. Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast cancer: improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov. (2019) 9:176–98. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1177 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

