Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ligases for Radiosensitization: From NEDDylation Inhibition to PROTACs
- PMID: 32983997
- PMCID: PMC7475704
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01517
Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ligases for Radiosensitization: From NEDDylation Inhibition to PROTACs
Abstract
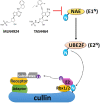
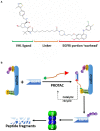
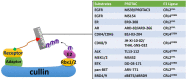
As a dynamic regulator for short-lived protein degradation and turnover, the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) plays important roles in various biological processes, including response to cellular stress, regulation of cell cycle progression, and carcinogenesis. Over the past decade, research on targeting the cullin-RING (really interesting new gene) E3 ligases (CRLs) in the UPS has gained great momentum with the entry of late-phase clinical trials of its novel inhibitors MLN4924 (pevonedistat) and TAS4464. Several preclinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of MLN4924 as a radiosensitizer, mainly due to its unique cytotoxic properties, including induction of DNA damage response, cell cycle checkpoints dysregulation, and inhibition of NF-κB and mTOR pathways. Recently, the PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) technology was developed to recruit the target proteins for CRL-mediated polyubiquitination, overcoming the resistance that develops inevitably with traditional targeted therapies. First-in-class cell-permeable PROTACs against critical radioresistance conferring proteins, including the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), androgen receptor (AR) and estrogen receptor (ER), cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1), and MEK2, have emerged in the past 5 years. In this review article, we will summarize the most important research findings of targeting CRLs for radiosensitization.
Keywords: EGFR; MLN4924; NEDDylation; PROTAC; cullin-RING E3 ligase.
Copyright © 2020 Zheng and Tao.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cullin-RING Ligases as attractive anti-cancer targets.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(18):3215-25. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990300. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23151137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Targeting Cullin-RING E3 ligases for anti-cancer therapy: efforts on drug discovery].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 May 25;49(1):1-19. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.02.21. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32621419 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Targeting Cullin-RING Ubiquitin Ligases and the Applications in PROTACs.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:317-347. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898236 Review.
-
Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 11;6:24218. doi: 10.1038/srep24218. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27063292 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of neddylation plays protective role in lipopolysaccharide-induced kidney damage through CRL-mediated NF-κB pathways.Am J Transl Res. 2019 May 15;11(5):2830-2842. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31217857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Chemo-Radiation-Resistance in Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 18;13:904063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.904063. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35662703 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Manifold role of ubiquitin in Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(10):4765-4783. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03816-8. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33825941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celecoxib Synergistically Enhances MLN4924-Induced Cytotoxicity and EMT Inhibition Via AKT and ERK Pathways in Human Urothelial Carcinoma.Cell Transplant. 2022 Jan-Dec;31:9636897221077921. doi: 10.1177/09636897221077921. Cell Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35176901 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in molecular targeted therapies to increase efficacy of (chemo)radiation therapy.Strahlenther Onkol. 2023 Dec;199(12):1091-1109. doi: 10.1007/s00066-023-02064-y. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Strahlenther Onkol. 2023. PMID: 37041372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on cullin neddylation and strategies to identify its inhibitors for cancer therapy.3 Biotech. 2022 Apr;12(4):103. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03162-x. Epub 2022 Mar 29. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35463041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anker CJ, Grossmann KF, Atkins MB, Suneja G, Tarhini AA, Kirkwood JM. Avoiding severe toxicity from combined BRAF inhibitor and radiation treatment: consensus guidelines from the eastern cooperative oncology group (ECOG). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2016) 95:632–46. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.01.038 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

