Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Osteosarcoma Treatment: Which Is the Key Target?
- PMID: 32984034
- PMCID: PMC7485562
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01642
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Osteosarcoma Treatment: Which Is the Key Target?
Abstract
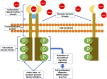
Recent clinical trials have shown several multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) to be effective in the treatment of osteosarcoma. However, these TKIs have a number of targets, and it is yet unclear which of these targets has a key role in osteosarcoma treatment. In this review, we first summarize the TKIs that were studied in clinical trials registered on ClinicalTrials.gov. Further, we compare and discuss the targets of these TKIs. We found that TKIs with promising therapeutic effect for osteosarcoma include apatinib, cabozantinib, lenvatinib, regorafenib, and sorafenib. The key targets for osteosarcoma treatment may include VEGFRs and RET. The receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) MET, IGF-1R, AXL, PDGFRs, KIT, and FGFRs might be relevant but unimportant targets for osteosarcoma treatment. Inhibition of one type of RTK for the treatment of osteosarcoma is not effective. It is necessary to inhibit several relevant RTKs simultaneously to achieve a breakthrough in osteosarcoma treatment. This review provides comprehensive information on TKI targets relevant in osteosarcoma treatment, and it will be useful for further research in this field.
Keywords: RET; RTKs; TKIs; VEGFRs; osteosarcoma; target therapy.
Copyright © 2020 Tian, Niu and Yao.
Figures


References
-
- Marina NM, Smeland S, Bielack SS, Bernstein M, Jovic G, Krailo MD, et al. . Comparison of MAPIE versus MAP in patients with a poor response to preoperative chemotherapy for newly diagnosed high-grade osteosarcoma (EURAMOS-1): an open-label, international, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17:1396–408. 10.1016/s1470-2045(16)30214-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

