Investigation of the role of herbal medicine, acupressure, and acupuncture in the menopausal symptoms: An evidence-based systematic review study
- PMID: 32984100
- PMCID: PMC7491766
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1094_19
Investigation of the role of herbal medicine, acupressure, and acupuncture in the menopausal symptoms: An evidence-based systematic review study
Abstract
Background: Menopause is an important physiological phenomenon in women's lives. Women's concern about taking the hormone treatment to ease menopausal symptoms is increasing. Over the past decade, the use of complementary and alternative medicine for the treatment of menopausal problems instead of hormone therapy has increased.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the role of herbal medicine, acupressure, and acupuncture in the menopausal symptoms.
Methods: Data source: related articles were searched from internal scientific databases and external databases of "Web of Scopus, Cochrane, PubMed, Science Direct, Ovid, and Google scholar."
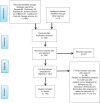
Study eligibility criteria: The keywords such as menopause, menopausal symptoms, complementary menopausal medicine, acupuncture in menopause, herbal medicine in menopause, and acupuncture in menopause were searched in the studies from 1987 to 2019. Exclusion criteria were inadequate information in the study, lack of access to full-text articles, animal studies, and reports. At the end of the search, 145 articles out of a total of 400 articles were reviewed.
Results: In various studies, different herbs such as licorice, valerian, soy, sage, ginseng, etc., were used to improve menopausal symptoms. In addition, acupuncture and acupressure were used to reduce menopausal symptoms.
Conclusion: The efficacy and use of complementary and alternative medicine, along with other classical medicine care, can be a new model for improving menopausal symptoms in women. It is recommended that further clinical and review studies be conducted to develop complementary and alternative medicine.
Keywords: Acupressure and acupuncture in the menopausal symptoms; herbal medicine.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the Complementary and Alternative Therapies for the Management of Psychological Symptoms of Menopause: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Menopausal Med. 2021 Dec;27(3):115-131. doi: 10.6118/jmm.21022. J Menopausal Med. 2021. PMID: 34989185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Acupuncture and Acupressure for Improving the Sleep Quality of Menopausal Women: A Meta-Analysis.Iran J Med Sci. 2025 Mar 1;50(3):132-145. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2024.102726.3586. eCollection 2025 Mar. Iran J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40224208 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary and alternative medicine for menopausal symptoms: a review of randomized, controlled trials.Ann Intern Med. 2002 Nov 19;137(10):805-13. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-137-10-200211190-00009. Ann Intern Med. 2002. PMID: 12435217 Review.
-
Influencing factors on women's attitudes toward hormone therapy acceptance for menopause treatment: a systematic review.Menopause. 2023 Oct 1;30(10):1061-1069. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002243. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Menopause. 2023. PMID: 37643393
-
A review of effective herbal medicines in controlling menopausal symptoms.Electron Physician. 2017 Nov 25;9(11):5826-5833. doi: 10.19082/5826. eCollection 2017 Nov. Electron Physician. 2017. PMID: 29403626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Health disorders in menopausal women: microbiome alterations, associated problems, and possible treatments.Biomed Eng Online. 2025 Jul 7;24(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12938-025-01415-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2025. PMID: 40624665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of ginseng on sexual function in postmenopausal women with major depression: a triple-blind randomized controlled trial.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2025 Jun 18;11(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40780-025-00461-2. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2025. PMID: 40533832 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Efficacy and Safety of Black Cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa) in Menopausal Symptom Management.J Midlife Health. 2024 Jan-Mar;15(1):5-11. doi: 10.4103/jmh.jmh_242_23. Epub 2024 Apr 4. J Midlife Health. 2024. PMID: 38764923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture: A Promising Approach for Comorbid Depression and Insomnia in Perimenopause.Nat Sci Sleep. 2021 Oct 12;13:1823-1863. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S332474. eCollection 2021. Nat Sci Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34675729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is CONSORT a Risk of Bias Tool for Experimental Studies: A Big Misunderstanding.J Caring Sci. 2025 Feb 11;14(1):1-4. doi: 10.34172/jcs.025.33575. eCollection 2025 Feb. J Caring Sci. 2025. PMID: 40391306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nappi RE, Kokot-Kierepa M. Women's voices in the menopause: Results from an international survey on vaginal atrophy. Maturitas. 2010;67:233–8. - PubMed
-
- Pérez JAM, Garcia FC, Palacios S, Pérez M. Epidemiology of risk factors and symptoms associated with menopause in Spanish women. Maturitas. 2009;62:30–6. - PubMed
-
- Russo R, Corosu R. The clinical use of a preparation based on phyto-oestrogens in the treatment of menopausal disorders. Acta Biomed. 2003;74:137–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous