New Insights Into Targeting Membrane Lipids for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 32984352
- PMCID: PMC7492565
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.571237
New Insights Into Targeting Membrane Lipids for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
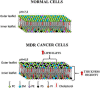
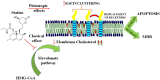
Modulation of membrane lipid composition and organization is currently developing as an effective therapeutic strategy against a wide range of diseases, including cancer. This field, known as membrane-lipid therapy, has risen from new discoveries on the complex organization of lipids and between lipids and proteins in the plasma membranes. Membrane microdomains present in the membrane of all eukaryotic cells, known as lipid rafts, have been recognized as an important concentrating platform for protein receptors involved in the regulation of intracellular signaling, apoptosis, redox balance and immune response. The difference in lipid composition between the cellular membranes of healthy cells and tumor cells allows for the development of novel therapies based on targeting membrane lipids in cancer cells to increase sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents and consequently defeat multidrug resistance. In the current manuscript strategies based on influencing cholesterol/sphingolipids content will be presented together with innovative ones, more focused in changing biophysical properties of the membrane bilayer without affecting the composition of its constituents.
Keywords: amphiphilic molecules; cell signaling; lipid rafts; membrane fluidity; protein receptors.
Copyright © 2020 Preta.
Figures
References
-
- Amin D., Cornell S. A., Gustafson S. K., Needle S. J., Ullrich J. W., Bilder G. E., et al. (1992). Bisphosphonates used for the treatment of bone disorders inhibit squalene synthase and cholesterol biosynthesis. J. Lipid Res. 33 1657–1663. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

