Individual and combined bioscore model of presepsin, procalcitonin, and high sensitive C - reactive protein as biomarkers for early diagnosis of paediatric sepsis
- PMID: 32984583
- PMCID: PMC7494471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04841
Individual and combined bioscore model of presepsin, procalcitonin, and high sensitive C - reactive protein as biomarkers for early diagnosis of paediatric sepsis
Abstract
Background: Paediatric sepsis remains a major public health problem with significant morbidity and mortality especially in developing countries. Clinical symptoms associated with sepsis are unreliable and laboratory parameters unspecific, making an early diagnosis of paediatric sepsis difficult. The lack of definitive biomarker(s) for early diagnosis of sepsis further leads to the misuse of antibiotics. Diagnosis based on a single biomarker does not provide adequate accuracy. Subsequently, combining multiple biomarkers into a single score will help clinicians make a better diagnostic judgment.
Aims: This study for the first time evaluated the individual and combined diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin (PCT), presepsin (sCD14-ST) and high sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) using a Bioscore model.
Materials and methods: In a case control study conducted at the Paediatric Emergency Unit (PEU) and the Mother and Baby Unit (MBU) of Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital (KATH), sixty (60) paediatric subjects aged zero to six (0-6) years, were diagnosed with sepsis using case-definition by the national neonatal bloodstream infection surveillance and Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Congress. Thirty (30) other paediatric subjects, aged and sex matched without sepsis or inflammatory conditions were used as controls. One-time blood sample was taken at the time of admission for blood culture and measurement of PCT, hs-CRP, and presepsin by ELISA. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS release 20.0, Copyright ©SPSS Inc.) was used for analysis.
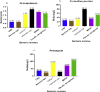
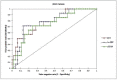
Results: Out of the sixty septic paediatric subjects, 14 patients (23.3%) had positive blood cultures (LCS) and 46 (76%) had negative for blood cultures (CS). Klebsiella spp. recorded the highest median levels of PCT, and hs-CRP while Pseudo. Aeruginasa recorded the highest of sCD14-ST levels. Significant elevations in PCT, sCD14-ST and hs-CRP levels were observed among septic cases in comparison to controls (p < 0.0001). Individually, PCT showed better accuracy (AUC = 78.7%) followed by hs-CRP (AUC = 78.4%) and sCD14-ST (AUC = 74.8%). Combination of PCT + hs-CRP had the highest accuracy (AUC = 80.1%) followed by hs-CRP + sCD14-ST (AUC = 77.2%), PCT + sCD14-ST + hs-CRP (AUC = 77.0%) and PCT + sCD14-ST (AUC = 75.9%).Conclusion: hs-CRP, PCT, and sCD14-ST are independent predictors of paediatric sepsis due to their high prognostic values. Moreover, Bioscore combination of these biomarkers was significantly associated with increased odds for sepsis. The incorporation of these biomarkers into routine diagnostic tests will aid in prompt diagnosis of paediatric sepsis.
Keywords: Bioscore model; High sensitive C-reactive protein; Immunology; Infectious disease; Musculoskeletal system; Paediatric sepsis; Paediatrics; Presepsin; Procalcitonin; Renal system; Reproductive system.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble CD14 subtype (sCD14-ST) presepsin in premature and full term critically ill newborns with sepsis and SIRS.Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Dec 7;451(Pt A):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.07.025. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26232159
-
Diagnostic accuracy of presepsin (sCD14-ST) as a biomarker of infection and sepsis in the emergency department.Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Jan;464:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.11.003. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Clin Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 27823951
-
Presepsin versus other biomarkers to predict sepsis and septic shock in patients with infection defined by Sepsis-3 criteria: the PREDI study of diagnostic accuracy.Emergencias. 2019 Oct;31(5):311-317. Emergencias. 2019. PMID: 31625302 English, Spanish.
-
The combination of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein or presepsin alone improves the accuracy of diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Crit Care. 2018 Nov 21;22(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2236-1. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30463590 Free PMC article.
-
Presepsin as a diagnostic marker of sepsis in children and adolescents: a systemic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):760. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4397-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31470804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Value of sIL-2R, TNF-α and PCT for Sepsis Infection in Patients With Closed Abdominal Injury Complicated With Severe Multiple Abdominal Injuries.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 22;12:741268. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.741268. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34745113 Free PMC article.
-
A study on bacteriological profile in suspected cases of neonatal sepsis and its correlation with various biomarkers in the rural population of a university hospital.J Family Med Prim Care. 2023 Oct;12(10):2313-2317. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_269_23. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Family Med Prim Care. 2023. PMID: 38074247 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoprotective potentialities of carvacrol and its nanoemulsion against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: development of nano-encasulation form.Heliyon. 2022 Mar 25;8(3):e09198. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09198. eCollection 2022 Mar. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35368529 Free PMC article.
-
Disease burden comparison and associated risk factors of early- and late-onset neonatal sepsis in China and the USA, 1990-2019.Glob Health Action. 2024 Dec 31;17(1):2396734. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2024.2396734. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Glob Health Action. 2024. PMID: 39229931 Free PMC article.
-
Criteria for Pediatric Sepsis-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis by the Pediatric Sepsis Definition Taskforce.Crit Care Med. 2022 Jan 1;50(1):21-36. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005294. Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 34612847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu L., Oza S., Hogan D., Perin J., Rudan I., Lawn J.E. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000-13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet (London, England) 2015;385(9966):430–440. - PubMed
-
- Chiesa C., Panero A., Osborn J.F., Simonetti A.F., Pacifico L. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a clinical and laboratory challenge. Clin. Chem. 2004;50(2):279–287. - PubMed
-
- Benitz W.E., Han M.Y., Madan A., Ramachandra P. Serial serum C-reactive protein levels in the diagnosis of neonatal infection. Pediatrics. 1998;102(4):E41. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes J.S. Clinicopathologic approach to the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Clin. Perinatol. 1991;18(2):361–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

