The role of biosensors in coronavirus disease-2019 outbreak
- PMID: 32984642
- PMCID: PMC7500281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coelec.2020.08.011
The role of biosensors in coronavirus disease-2019 outbreak
Abstract
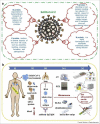
Herein, we have summarized and argued about biomarkers and indicators used for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Antibody detection methods are not considered suitable to screen individuals at early stages and asymptomatic cases. The diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 using biomarkers and indicators at point-of-care level is much crucial. Therefore, it is urgently needed to develop rapid and sensitive detection methods which can target antigens. We have critically elaborated key role of biosensors to cope the outbreak situation. In this review, the importance of biosensors including electrochemical, surface enhanced Raman scattering, field-effect transistor, and surface plasmon resonance biosensors in the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has been underscored. Finally, we have outlined pros and cons of diagnostic approaches and future directions.
Keywords: Diagnostics; Electrochemical biosensors; Field-effect transistor biosensors; Plasmonic biosensors; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
