Artificial intelligence in COVID-19 drug repurposing
- PMID: 32984792
- PMCID: PMC7500917
- DOI: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30192-8
Artificial intelligence in COVID-19 drug repurposing
Abstract
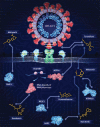
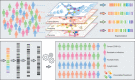
Drug repurposing or repositioning is a technique whereby existing drugs are used to treat emerging and challenging diseases, including COVID-19. Drug repurposing has become a promising approach because of the opportunity for reduced development timelines and overall costs. In the big data era, artificial intelligence (AI) and network medicine offer cutting-edge application of information science to defining disease, medicine, therapeutics, and identifying targets with the least error. In this Review, we introduce guidelines on how to use AI for accelerating drug repurposing or repositioning, for which AI approaches are not just formidable but are also necessary. We discuss how to use AI models in precision medicine, and as an example, how AI models can accelerate COVID-19 drug repurposing. Rapidly developing, powerful, and innovative AI and network medicine technologies can expedite therapeutic development. This Review provides a strong rationale for using AI-based assistive tools for drug repurposing medications for human disease, including during the COVID-19 pandemic.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license.
Figures

References
-
- Turing AM. Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind. 1950;49:433–460.
-
- Fleming N. How artificial intelligence is changing drug discovery. Nature. 2018;557:S55–S57. - PubMed
-
- Smalley E. AI-powered drug discovery captures pharma interest. Nat Biotechnol. 2017;35:604–605. - PubMed
-
- Avorn J. The $2·6 billion pill·methodologic and policy considerations. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1877–1879. - PubMed
-
- Chong CR, Sullivan DJ., Jr New uses for old drugs. Nature. 2007;448:645–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

