[Effects of Physical Activity on Health]
- PMID: 32984942
- PMCID: PMC7521632
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1217-0549
[Effects of Physical Activity on Health]
Abstract
Regular physical activity contributes to both maintaining and improving health, and is important for human development throughout the entire lifespan of a person. There is strong evidence for the beneficial effects of physical activity on health, in the areas of all-cause mortality, cancer, cardiovascular health, musculoskeletal health, metabolic health, and neurocognitive health. Physical activity includes any form of movement in which the contraction of skeletal muscles results in an increase in energy consumption. It is quantified and controlled via the frequency, duration, intensity, and weekly extent. All those forms of movement that improve health and in which the risk of injury is low are defined as health-enhancing physical activity. The Austrian recommendations for health-enhancing physical activity include endurance-oriented movement, plus strength and coordination training. Exercise is aimed at initiating adaptation processes, in order to improve functionality. Therefore, it has to be adapted to the different levels of individual performance ability, activity levels, and age, and should be carried out according to certain principles. Exercise leads to a positive change in physiological parameters, which in turn are closely linked to an improvement in the state of health. Through regular endurance-oriented and muscle-strengthening physical activity, far-reaching health effects can be achieved. Nevertheless, undesirable events can occur during activity, and the musculoskeletal and circulatory systems can be particularly affected. However, through adequate preparation, suitable equipment, and appropriate exercise, the personal and also the public health benefits of physical activity and sport can be increased.
Regelmäßige Bewegung trägt sowohl zum Erhalt als auch zur Verbesserung des Gesundheitszustandes bei und ist für die menschliche Entwicklung über die gesamte Lebensspanne des Menschen wichtig. Starke Evidenz hinsichtlich der positiven Auswirkung körperlicher Aktivität auf die Gesundheit liegt in den Bereichen Gesamtsterblichkeit, Krebserkrankungen, Herz-Kreislaufgesundheit, muskuloskelettale Gesundheit, Stoffwechselgesundheit sowie neurokognitive Gesundheit vor. Körperliche Aktivität umfasst jede Form von Bewegung, bei der durch die Kontraktion der Skelettmuskulatur eine Erhöhung des Energieverbrauchs erzielt wird. Sie wird über die Belastungskomponenten Häufigkeit, Dauer, Intensität und Wochenumfang quantifiziert und gesteuert. Als gesundheitswirksame körperliche Aktivität werden all jene Bewegungsformen bezeichnet, welche die Gesundheit verbessern und bei denen das Verletzungsrisiko gering ist. In den Österreichischen Bewegungsempfehlungen werden ausdauerorientierte Bewegung, Krafttraining und Koordinationsübungen empfohlen. Training nimmt innerhalb der gesundheitswirksamen körperlichen Aktivität eine Sonderstellung ein. Es zielt darauf ab, Anpassungsvorgänge im Körper in Gang zu setzen, um Körperfunktionen zu verbessern. Dabei muss die Aktivität an die unterschiedliche individuelle Leistungsfähigkeit, das Aktivitätsniveau und das Alter angepasst und nach bestimmten Grundsätzen durchgeführt werden. Durch das Training kommt es zu einer positiven Veränderung physiologischer Parameter, die wiederum in enger Verbindung mit einer Verbesserung des Gesundheitszustandes steht. Durch regelmäßige ausdauerorientierte und muskelkräftigende Bewegung werden weitreichende Gesundheitseffekte erzielt. Dennoch kann es bei der Ausführung zu unerwünschten Ereignissen kommen. Hiervon betroffen sind v. a. der Bewegungsapparat und das Kreislaufsystem. Durch adäquate Vorbereitung, passende Ausrüstung und richtige Ausübung wird jedoch nicht nur der persönliche, sondern auch der gemeinschaftliche Gesundheitsnutzen durch Bewegung und Sport gesteigert.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Die Autorinnen und Autoren geben an, dass kein Interessenkonflikt besteht.
Figures
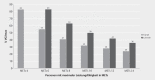

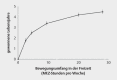
References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans Washington DC: U.S: Department of Health and Human Services; 2008
-
- Ekelund U et al.Does physical activity attenuate, or even eliminate, the detrimental association of sitting time with mortality? A harmonised meta-analysis of data from more than 1 million men and women. The Lancet. 2016;388:1302–1310. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Scientific Report Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018
-
- Weineck Jürgen.Optimales Training: Leistungsphysiologische Trainingslehre unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des Kinder- und Jugendtrainings 17 th ed. 16. Auflage. Erlangen: Spitta; 2019

