Balancing selection versus allele and supertype turnover in MHC class II genes in guppies
- PMID: 32985616
- PMCID: PMC8027376
- DOI: 10.1038/s41437-020-00369-7
Balancing selection versus allele and supertype turnover in MHC class II genes in guppies
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Balancing selection versus allele and supertype turnover in MHC class II genes in guppies.Heredity (Edinb). 2021 Mar;126(3):561. doi: 10.1038/s41437-021-00407-y. Heredity (Edinb). 2021. PMID: 33564182 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
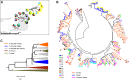
Selection pressure from parasites is thought to be a major force shaping the extreme polymorphism of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes, but the modes and consequences of selection remain unclear. Here, we analyse MHC class II and microsatellite diversity in 16 guppy (Poecilia reticulata) populations from two islands (Trinidad and Tobago) that have been separated for at least 10 ky. Within-population MHC diversity was high, but allele sharing was limited within islands and even lower between islands, suggesting relatively fast turnover of alleles. Allelic lineages strongly supported in phylogenetic analyses tended to be island-specific, suggesting rapid lineage sorting, and an expansion of an allelic lineage private to Tobago was observed. New alleles appear to be generated locally at a detectably high frequency. We did not detect a consistent signature of local adaptation, but FST outlier analysis suggested that balancing selection may be the more general process behind spatial variation in MHC allele frequencies in this system, particularly within Trinidad. We found no evidence for divergent allele advantage within populations, or for decreased genetic structuring of MHC supertypes compared to MHC alleles. The dynamic and complex nature of MHC evolution we observed in guppies, coupled with some evidence for balancing selection shaping MHC allele frequencies, are consistent with Red Queen processes of host-parasite coevolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Aguilar A, Garza JC. A comparison of variability and population structure for major histocompatibility complex and microsatellite loci in California coastal steelhead (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) Mol Ecol. 2006;15(4):923–937. - PubMed
-
- Alexander HJ, Taylor JS, Wu SS-T, Breden F. Parallel evolution and vicariance in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata) over multiple spatial and temporal scales. Evolution. 2006;60(11):2352–2369. - PubMed
-
- Apanius V, Penn D, Slev PR, Ruff LR, Potts WK. The nature of selection on the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol. 1997;17(2):179–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

