COVID-19: A Greek Perspective
- PMID: 32985717
- PMCID: PMC7549190
- DOI: 10.1111/jocs.15027
COVID-19: A Greek Perspective
Abstract
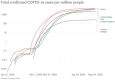
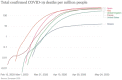
Greece has managed to timely and properly implement a public health safety plan and contained the burden of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. On the contrary, COVID-19 has led to a national catastrophe in countries with superior infrastructures, such as Italy, Spain, France, and the United States. At a time when our nation's healthcare resources were insufficient to meet this unprecedented demand, it was necessary to prioritize needs in the hopes of maximizing lives saved. Although delaying definitive treatment of disorders presented a risk to specific individuals, countless others afforded life-saving resources necessary to overcome the most threatening manifestation of this illness. The cataclysm of COVID-19 offered an opportunity to reshape health care in ways that may not have seemed possible just a few months ago. To help scientists and clinicians across disciplines connect their strengths, so that together we can advance the state of the art in medicine and lead the way to a new era of computational medicine.
Keywords: COVID-19; Greece; cardiac surgery; coronavirus.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 pandemic: challenges and opportunities for the Greek health care system.Ir J Psychol Med. 2020 Sep;37(3):226-230. doi: 10.1017/ipm.2020.35. Epub 2020 May 14. Ir J Psychol Med. 2020. PMID: 32406360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Analysis of the development trend and severity of the COVID-19 panidemic in the global world].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Jun 18;53(3):536-542. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.016. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 34145857 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Living with covid-19.Psychiatriki. 2020 Jul-Sep;31(3):197-200. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2020.313.197. Psychiatriki. 2020. PMID: 33099460 English, Greek, Modern.
-
A Reminder of Skin Cancer During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021 Apr;291(1):58. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021. PMID: 34477068
-
Novel 2019 coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): an overview for emergency clinicians.Pediatr Emerg Med Pract. 2020 May 2;17(5):1-24. Print 2020 May. Pediatr Emerg Med Pract. 2020. PMID: 32286766 Review.
Cited by
-
Information seeking behavior and COVID-19 pandemic: A snapshot of young, middle aged and senior individuals in Greece.Int J Med Inform. 2021 Jun;150:104465. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2021.104465. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Int J Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 33887589 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic in Sleep Quality and Lifestyle in Young Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 28;19(19):12333. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912333. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2019 Novel Coronavirus COVID‐19 (2019‐nCoV) Data Repository by Johns Hopkins CSSE [Internet]. https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID19/blob/master/csse_covid_19_data.... Accessed March 18, 2020.
-
- Report of the WHO‐China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) [Internet]. Geneva: WHO; 28 Feb 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mis.... Accessed March 18, 2020.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of patients with confirmed coronavirus diseases (COVID‐19) [Internet]. CDC: Healthcare Professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-manageme.... Accessed March 18, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical