Accuracy of Physicians' Electrocardiogram Interpretations: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 32986084
- PMCID: PMC7522782
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3989
Accuracy of Physicians' Electrocardiogram Interpretations: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Importance: The electrocardiogram (ECG) is the most common cardiovascular diagnostic test. Physicians' skill in ECG interpretation is incompletely understood.
Objectives: To identify and summarize published research on the accuracy of physicians' ECG interpretations.
Data sources: A search of PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane CENTRAL (Central Register of Controlled Trials), PsycINFO, CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health), ERIC (Education Resources Information Center), and Web of Science was conducted for articles published from database inception to February 21, 2020.
Study selection: Of 1138 articles initially identified, 78 studies that assessed the accuracy of physicians' or medical students' ECG interpretations in a test setting were selected.
Data extraction and synthesis: Data on study purpose, participants, assessment features, and outcomes were abstracted, and methodological quality was appraised with the Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument. Results were pooled using random-effects meta-analysis.
Main outcomes and measures: Accuracy of ECG interpretation.
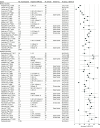
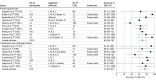
Results: Of 1138 studies initially identified, 78 assessed the accuracy of ECG interpretation. Across all training levels, the median accuracy was 54% (interquartile range [IQR], 40%-66%; n = 62 studies) on pretraining assessments and 67% (IQR, 55%-77%; n = 47 studies) on posttraining assessments. Accuracy varied widely across studies. The pooled accuracy for pretraining assessments was 42.0% (95% CI, 34.3%-49.6%; n = 24 studies; I2 = 99%) for medical students, 55.8% (95% CI, 48.1%-63.6%; n = 37 studies; I2 = 96%) for residents, 68.5% (95% CI, 57.6%-79.5%; n = 10 studies; I2 = 86%) for practicing physicians, and 74.9% (95% CI, 63.2%-86.7%; n = 8 studies; I2 = 22%) for cardiologists.
Conclusions and relevance: Physicians at all training levels had deficiencies in ECG interpretation, even after educational interventions. Improved education across the practice continuum appears warranted. Wide variation in outcomes could reflect real differences in training or skill or differences in assessment design.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Physicians' Electrocardiogram Interpretations.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 May 1;181(5):721. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8598. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33523089 No abstract available.
-
Physicians' Electrocardiogram Interpretations.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 May 1;181(5):721-722. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8605. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33523117 No abstract available.
-
Physicians' Electrocardiogram Interpretations-Reply.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 May 1;181(5):722-723. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8652. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33523118 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kligfield P, Gettes LS, Bailey JJ, et al. ; American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; American College of Cardiology Foundation; Heart Rhythm Society . Recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part I: the electrocardiogram and its technology: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society: endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Circulation. 2007;115(10):1306-1324. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.180200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salerno SM, Alguire PC, Waxman HS; American College of Physicians . Training and competency evaluation for interpretation of 12-lead electrocardiograms: recommendations from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(9):747-750. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-138-9-200305060-00012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Family Physicians Electrocardiograms, family physician interpretation (position paper). Accessed February 14, 2020. https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/electrocardiograms.html
-
- Antiperovitch P, Zareba W, Steinberg JS, et al. . Proposed in-training electrocardiogram interpretation competencies for undergraduate and postgraduate trainees. J Hosp Med. 2018;13(3):185-193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

