Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Cancer Care: A Global Collaborative Study
- PMID: 32986516
- PMCID: PMC7529504
- DOI: 10.1200/GO.20.00351
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Cancer Care: A Global Collaborative Study
Abstract
Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic affected health care systems globally and resulted in the interruption of usual care in many health care facilities, exposing vulnerable patients with cancer to significant risks. Our study aimed to evaluate the impact of this pandemic on cancer care worldwide.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study using a validated web-based questionnaire of 51 items. The questionnaire obtained information on the capacity and services offered at these centers, magnitude of disruption of care, reasons for disruption, challenges faced, interventions implemented, and the estimation of patient harm during the pandemic.
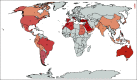
Results: A total of 356 centers from 54 countries across six continents participated between April 21 and May 8, 2020. These centers serve 716,979 new patients with cancer a year. Most of them (88.2%) reported facing challenges in delivering care during the pandemic. Although 55.34% reduced services as part of a preemptive strategy, other common reasons included an overwhelmed system (19.94%), lack of personal protective equipment (19.10%), staff shortage (17.98%), and restricted access to medications (9.83%). Missing at least one cycle of therapy by > 10% of patients was reported in 46.31% of the centers. Participants reported patient exposure to harm from interruption of cancer-specific care (36.52%) and noncancer-related care (39.04%), with some centers estimating that up to 80% of their patients were exposed to harm.
Conclusion: The detrimental impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer care is widespread, with varying magnitude among centers worldwide. Additional research to assess this impact at the patient level is required.
Conflict of interest statement
Abdul Rahman Jazieh
Giuseppe Curigliano
Evangelia D. Razis
Hassan Errihani
Roselle B. De Guzman
Christian Rolfo
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394-424, 2018 [Erratum: CA Cancer J Clin 70:313, 2020] - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization: WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....