Lack of NFATc1 SUMOylation prevents autoimmunity and alloreactivity
- PMID: 32986812
- PMCID: PMC7953626
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20181853
Lack of NFATc1 SUMOylation prevents autoimmunity and alloreactivity
Abstract
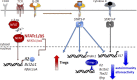
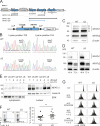
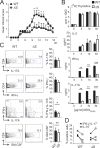
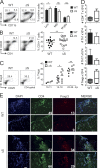
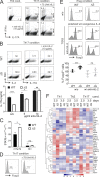
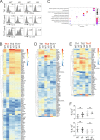
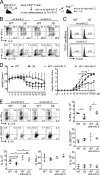
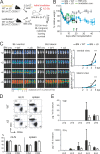
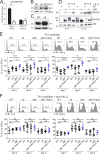
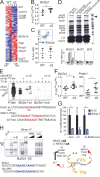
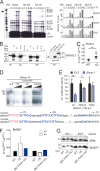
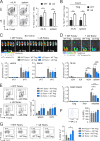
Posttranslational modification with SUMO is known to regulate the activity of transcription factors, but how SUMOylation of individual proteins might influence immunity is largely unexplored. The NFAT transcription factors play an essential role in antigen receptor-mediated gene regulation. SUMOylation of NFATc1 represses IL-2 in vitro, but its role in T cell-mediated immune responses in vivo is unclear. To this end, we generated a novel transgenic mouse in which SUMO modification of NFATc1 is prevented. Avoidance of NFATc1 SUMOylation ameliorated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis as well as graft-versus-host disease. Elevated IL-2 production in T cells promoted T reg expansion and suppressed autoreactive or alloreactive immune responses. Mechanistically, increased IL-2 secretion counteracted IL-17 and IFN-γ expression through STAT5 and Blimp-1 induction. Then, Blimp-1 repressed IL-2 itself, as well as the induced, proliferation-associated survival factor Bcl2A1. Collectively, these data demonstrate that prevention of NFATc1 SUMOylation fine-tunes T cell responses toward lasting tolerance. Thus, targeting NFATc1 SUMOylation presents a novel and promising strategy to treat T cell-mediated inflammatory diseases.
© 2020 Xiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: L. Dietz reported other funding from Pfizer Pharma GmbH outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NFATc1/αA and Blimp-1 Support the Follicular and Effector Phenotype of Tregs.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 6;12:791100. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.791100. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069572 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase B/Akt signals impair Th17 differentiation and support natural regulatory T cell function and induced regulatory T cell formation.J Immunol. 2009 Nov 15;183(10):6124-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900246. Epub 2009 Oct 19. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19841181
-
Selective Impairment of TH17-Differentiation and Protection against Autoimmune Arthritis after Overexpression of BCL2A1 in T Lymphocytes.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 19;11(7):e0159714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159714. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27433938 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation of a small isoform of NFATc1 is promoted by PIAS proteins and inhibits transactivation activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 May 21;513(1):172-178. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.171. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30952432
-
NFATc1 induction in peripheral T and B lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 1;190(5):2345-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201591. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23365084
Cited by
-
NFATc1/αA and Blimp-1 Support the Follicular and Effector Phenotype of Tregs.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 6;12:791100. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.791100. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069572 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular therapies for the prevention and treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease.Stem Cells. 2025 May 27;43(6):sxaf009. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf009. Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40117296 Review.
-
Immune regulation by the SUMO family.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Aug;25(8):608-620. doi: 10.1038/s41577-025-01155-4. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40108400 Review.
-
The emerging roles of SUMOylation in the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jul 6;12(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00420-3. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37415251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BLIMP1 negatively regulates IL-2 signaling in T cells.Sci Adv. 2025 Jul 18;11(29):eadx8105. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adx8105. Epub 2025 Jul 18. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40680114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beilhack, A., Schulz S., Baker J., Beilhack G.F., Wieland C.B., Herman E.I., Baker E.M., Cao Y.A., Contag C.H., and Negrin R.S.. 2005. In vivo analyses of early events in acute graft-versus-host disease reveal sequential infiltration of T-cell subsets. Blood. 106:1113–1122. 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0509 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berberich-Siebelt, F., Berberich I., Andrulis M., Santner-Nanan B., Jha M.K., Klein-Hessling S., Schimpl A., and Serfling E.. 2006. SUMOylation interferes with CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta-mediated c-myc repression, but not IL-4 activation in T cells. J. Immunol. 176:4843–4851. 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.4843 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berberich-Siebelt, F., Klein-Hessling S., Hepping N., Santner-Nanan B., Lindemann D., Schimpl A., Berberich I., and Serfling E.. 2000. C/EBPbeta enhances IL-4 but impairs IL-2 and IFN-gamma induction in T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 30:2576–2585. 10.1002/1521-4141(200009)30:9<2576::AID-IMMU2576>3.0.CO;2-N - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

