Clinical and genetic determinants of urinary glucose excretion in patients with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 32986906
- PMCID: PMC8088999
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13417
Clinical and genetic determinants of urinary glucose excretion in patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Glucosuria is a representative symptom in diabetes patients with poor glycemic control and in those treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Renal threshold levels of glucose excretion are known to vary among individuals, but factors contributing to glucosuria are not well characterized. The present study aimed to clarify clinical and genetic determinants of glucosuria in individuals with diabetes mellitus.
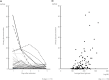
Materials and methods: The 24-h urinary glucose excretion was measured in 135 hospitalized patients on admission, with continuous measurement for five consecutive days in 75 patients. Genetic and clinical factors contributing to glucosuria were studied. As a genetic factor, SLC5A2 polymorphism was genotyped. A total of 476 participants (266 participants with type 2 diabetes and 210 healthy controls) were additionally genotyped for the association study of SLC5A2 with type 2 diabetes. A meta-analysis was carried out with the present study and previous association studies.
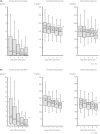
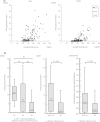
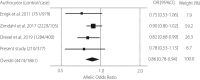
Results: Multiple regression analysis showed that the independent variables of average blood glucose (β = 0.41, P = 1.4 × 10-7 ), estimated glomerular filtration rate (β = 0.28, P = 6.0 × 10-5 ), sex (β = 0.28, P = 5.7 × 10-5 ) and SLC5A2 rs9934336 polymorphism (β = 0.17, P = 0.02) were significantly correlated with urinary glucose excretion. The frequency of the A allele of rs9934336 tended to be lower in participants with type 2 diabetes than in controls (odds ratio 0.78, 95% confidence interval 0.53-1.13, not significant), and meta-analysis showed a significant association between the A allele and type 2 diabetes (summary odds ratio for minor allele [A] 0.86, 95% confidence interval 0.78-0.94, P < 0.002).
Conclusions: Blood glucose, estimated glomerular filtration rate, sex and SLC5A2 polymorphism were independent determinants of glucosuria in diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: SLC5A2; Diabetes mellitus; Glucosuria.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
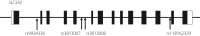
References
-
- Gerich JE, Meyer C, Woerle HJ, et al. Renal gluconeogenesis: Its importance in human glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 382–391. - PubMed
-
- Gamba G, Miyanoshita A, Lombardi M, et al. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and characterization of two members of the mammalian electroneutral sodium‐(potassium)‐chloride cotransporter family expressed in kidney. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 17713–17722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 17K09852/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
- 18K08493/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
- 18K08530/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

