Bronchial Fistula: Rare Complication of Treatment with Anlotinib
- PMID: 32987493
- PMCID: PMC7583880
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.102.40
Bronchial Fistula: Rare Complication of Treatment with Anlotinib
Abstract
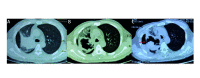
Background: Anlotinib is a newly developed small molecule multiple receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that was approved for the treatment of patients with lung cancer in China. We aim to report 3 cases of rare complication of anlotinib-bronchial fistula (BF) during the treatment of lung cancer patients and summarize the possible causes.
Methods: We collected three patients who developed BF due to anlotinib treatment, and conducted a search of Medline and PubMed for medical literature published between 2018 and 2020 using the following search terms: "anlotinib," "lung cancer," and "fistula."
Results: Our literature search produced two case reports (three patients) which, in addition to our three patients. We collated the patients' clinical characteristics including demographic information, cancer type, imaging features, treatment received, risk factors for anlotinib related BF, and treatment-related outcomes. The six patients shared some common characteristics: advanced age, male, concurrent infection symptoms, diabetes mellitus (DM), advanced squamous cell and small cell lung cancers, centrally located tumors, tumor measuring ≥5 cm in longest diameter, and newly formed tumor cavitation after multi-line treatment especially after receiving radiotherapy. Fistula types included broncho-pericardial fistula, broncho-pleural fistula, and esophago-tracheobronchial fistula. Six patients all died within 6 months.
Conclusions: Although anlotinib is relatively safe, it is still necessary to pay attention to the occurrence of BF, a rare treatment side effect that threatens the quality of life and overall survival of patients. Anlotinib, therefore, requires selective use and close observation of high-risk patients.
Keywords: Anlotinib; Bronchial fistula; Broncho-pericardial fistula; Broncho-pleural fistula; Esophago-tracheobronchial fistula; Lung neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
China National Medical Products Administration approval summary: anlotinib for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer after two lines of chemotherapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019 Jun 20;39(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0383-7. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31221221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Anlotinib Alone and in Combination with Other Drugs in Advanced Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Feb 25;2022:1475871. doi: 10.1155/2022/1475871. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9789208. doi: 10.1155/2023/9789208. PMID: 35251294 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Anlotinib-containing regimen for advanced small-cell lung cancer: A protocol of meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 11;16(3):e0247494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247494. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33705427 Free PMC article.
-
Anlotinib: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2018 Jul;78(10):1057-1062. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0939-x. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29943374 Review.
-
Response to first-line treatment predicts progression-free survival benefit of small-cell lung cancer patients treated with anlotinib.Cancer Med. 2021 Jun;10(12):3896-3904. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3941. Epub 2021 May 6. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33960145 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

