The Risk of Systemic Diseases in Those with Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: From Mechanisms to Clinic
- PMID: 32987907
- PMCID: PMC7583918
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197041
The Risk of Systemic Diseases in Those with Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: From Mechanisms to Clinic
Abstract
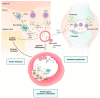
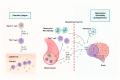
Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) have been recently considered as chronic systemic inflammatory disorders. Over the past decades, enormous evidence indicates that patients with psoriasis and PsA have a higher risk of developing various comorbidities including cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease, cancers, infections, autoimmune disease, and psychiatric diseases. However, reported risks of some comorbidities in those with psoriasis and PsA are somewhat different according to the research design. Moreover, pathomechanisms underlying comorbidities of those with psoriasis and PsA remain poorly elucidated. The purpose of this review is to provide the most updated comprehensive view of the risk of systemic comorbidities in those with psoriasis and PsA. Molecular mechanisms associated with the development of various comorbidities in those with psoriasis and PsA are also reviewed based on recent laboratory and clinical investigations. Identifying the risk of systemic comorbidities and its associated pathomechanisms in those with psoriasis and PsA could provide a sufficient basis to use a multi-disciplinary approach for treating patients with psoriasis and PsA.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; cancer; cardiovascular disease; comorbidity; infection; metabolic syndrome; psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis; sleep disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Strauss H. Zur Lehre von der neurogenen und der thyreogenen Glykosurie. DMW Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1897;23:275–278.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

