The Implementation Research Logic Model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects
- PMID: 32988389
- PMCID: PMC7523057
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-020-01041-8
The Implementation Research Logic Model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects
Abstract
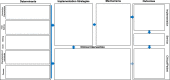
Background: Numerous models, frameworks, and theories exist for specific aspects of implementation research, including for determinants, strategies, and outcomes. However, implementation research projects often fail to provide a coherent rationale or justification for how these aspects are selected and tested in relation to one another. Despite this need to better specify the conceptual linkages between the core elements involved in projects, few tools or methods have been developed to aid in this task. The Implementation Research Logic Model (IRLM) was created for this purpose and to enhance the rigor and transparency of describing the often-complex processes of improving the adoption of evidence-based interventions in healthcare delivery systems.
Methods: The IRLM structure and guiding principles were developed through a series of preliminary activities with multiple investigators representing diverse implementation research projects in terms of contexts, research designs, and implementation strategies being evaluated. The utility of the IRLM was evaluated in the course of a 2-day training to over 130 implementation researchers and healthcare delivery system partners.
Results: Preliminary work with the IRLM produced a core structure and multiple variations for common implementation research designs and situations, as well as guiding principles and suggestions for use. Results of the survey indicated a high utility of the IRLM for multiple purposes, such as improving rigor and reproducibility of projects; serving as a "roadmap" for how the project is to be carried out; clearly reporting and specifying how the project is to be conducted; and understanding the connections between determinants, strategies, mechanisms, and outcomes for their project.
Conclusions: The IRLM is a semi-structured, principle-guided tool designed to improve the specification, rigor, reproducibility, and testable causal pathways involved in implementation research projects. The IRLM can also aid implementation researchers and implementation partners in the planning and execution of practice change initiatives. Adaptation and refinement of the IRLM are ongoing, as is the development of resources for use and applications to diverse projects, to address the challenges of this complex scientific field.
Keywords: Integration; Logic models; Program theory; Study specification.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Comment in
-
Letter to the editor on "the implementation research logic model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects" (Smith JD, Li DH, Rafferty MR. the implementation research logic model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects. Implement Sci. 2020;15 (1):84. Doi:10.1186/s13012-020-01041-8).Implement Sci. 2021 Nov 17;16(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13012-021-01169-1. Implement Sci. 2021. PMID: 34789294 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Smith JD. An Implementation Research Logic Model: a step toward improving scientific rigor, transparency, reproducibility, and specification. Implement Sci. 2018;14:S39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

