Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Functions in Gram-Positive Bacteria
- PMID: 32989035
- PMCID: PMC7671900
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00433-20
Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Functions in Gram-Positive Bacteria
Abstract
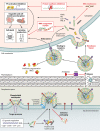
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-derived lipid bilayers secreted by bacteria and eukaryotic cells. Bacterial membrane vesicles were discovered over 60 years ago and have been extensively studied in Gram-negative bacteria. During their production, EVs are loaded with proteins, nucleic acids, and various compounds that are subsequently released into the environment. Depending on the packaged cargo, EVs have a broad spectrum of action and are involved in pathogenesis, antibiotic resistance, nutrient uptake, and nucleic acid transfer. Due to differences in cell wall structure, EVs in Gram-positive bacteria have been disregarded for decades, and our understanding of their biogenesis and host cell interaction is incomplete. Recently, studies on bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus spp., Bacillus subtilis, and Mycobacterium spp. have demonstrated EV production in Gram-positive bacteria and shown the great importance EVs have in Gram-positive bacterial physiology and disease progression. Here, we review the latest findings on the biogenesis and functions of EVs from Gram-positive bacteria and identify key areas for future research.
Keywords: EVs; Gram-positive bacteria; OMV; extracellular vesicles; membrane vesicles.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

