Serial Prefrontal Pathways Are Positioned to Balance Cognition and Emotion in Primates
- PMID: 32989097
- PMCID: PMC7577604
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0860-20.2020
Serial Prefrontal Pathways Are Positioned to Balance Cognition and Emotion in Primates
Abstract
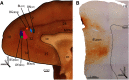
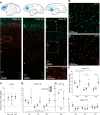
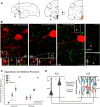
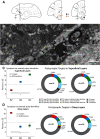
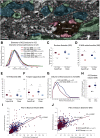
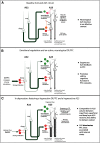
The delicate balance among primate prefrontal networks is necessary for homeostasis and behavioral flexibility. Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) is associated with cognition, while the most ventromedial subgenual cingulate area 25 (A25) is associated with emotion and emotional expression. Yet A25 is weakly connected with dlPFC, and it is unknown how the two regions communicate. In rhesus monkeys of both sexes, we investigated how these functionally distinct areas may interact through pregenual anterior cingulate area 32 (A32), which is strongly connected with both. We found that dlPFC innervated the deep layers of A32, while A32 innervated all layers of A25, mostly targeting spines of excitatory neurons. Approximately 20% of A32 terminations formed synapses on inhibitory neurons in A25, notably the powerful parvalbumin inhibitory neurons in the deep layers, and the disinhibitory calretinin neurons in the superficial layers. By innervating distinct inhibitory microenvironments in laminar compartments, A32 is positioned to tune activity in columns of A25. The circuitry of the sequential pathway indicates that when dlPFC is engaged, A32 can dampen A25 output through the parvalbumin inhibitory microsystem in the deep layers of A25. A32 thus may flexibly recruit or reduce activity in A25 to maintain emotional equilibrium, a process that is disrupted in depression. Moreover, pyramidal neurons in A25 had a heightened density of NMDARs, which are the targets of novel rapid-acting antidepressants. Pharmacologic antagonism of NMDARs in patients with depression may reduce excitability in A25, mimicking the effects of the neurotypical serial pathway identified here.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT The anterior cingulate is a critical hub in prefrontal networks through connections with functionally distinct areas. Dorsolateral and polar prefrontal areas that are associated with complex cognition are connected with the anterior cingulate in a pattern that allows them to indirectly control downstream activity from the anterior cingulate to the subgenual cingulate, which is associated with heightened activity and negative affect in depression. This set of pathways provides a circuit mechanism for emotional regulation, with the anterior cingulate playing a balancing role for integration of cognitive and emotional processes. Disruption of these pathways may perturb network function and the ability to regulate cognitive and affective processes based on context.
Keywords: anterior cingulate; depression; dlPFC; inhibitory neurons; laminar connections; subgenual cingulate.
Copyright © 2020 the authors.
Figures






References
-
- Alexander L, Gaskin PL, Sawiak SJ, Fryer TD, Hong YT, Cockcroft GJ, Clarke HF, Roberts AC (2019b) Fractionating blunted reward processing characteristic of anhedonia by over-activating primate subgenual anterior cingulate cortex. Neuron 101:307–320.e306. 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
