Antinociceptive role of neurotensin receptor 1 in rats with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 32989196
- PMCID: PMC7532295
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.4.318
Antinociceptive role of neurotensin receptor 1 in rats with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a major side effect of anti-cancer drugs. Neurotensin receptors (NTSRs) are widely distributed within the pain circuits in the central nervous system. The purpose of this study was to determine the role of NTSR1 by examining the effects of an NTSR1 agonist in rats with CIPN and investigate the contribution of spinal serotonin receptors to the antinociceptive effect.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats (weight 150-180 g) were used in this study. CIPN was induced by injecting cisplatin (2 mg/kg) once a day for 4 days. Intrathecal catheters were placed into the subarachnoid space of the CIPN rats. The antiallodynic effects of intrathecally or intraperitoneally administered PD 149163, an NTSR1 agonist, were evaluated. Furthermore, the levels of serotonin in the spinal cord were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography.
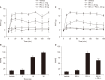
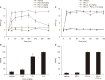
Results: Intrathecal or intraperitoneal PD 149163 increased the paw withdrawal threshold in CIPN rats. Intrathecal administration of the NTSR1 antagonist SR 48692 suppressed the antinociceptive effect of PD 149163 given via the intrathecal route, but not the antinociceptive effect of intraperitoneally administered PD 149163. Intrathecal administration of dihydroergocristine, a serotonin receptor antagonist, suppressed the antinociceptive effect of intrathecally administered, but not intraperitoneally administered, PD 149163. Injecting cisplatin diminished the serotonin level in the spinal cord, but intrathecal or intraperitoneal administration of PD 149163 did not affect this reduction.
Conclusions: NTSR1 played a critical role in modulating CIPN-related pain. Therefore, NTSR1 agonists may be useful therapeutic agents to treat CIPN. In addition, spinal serotonin receptors may be indirectly involved in the effect of NTSR1 agonist.
Keywords: Cisplatin; Dihydroergocristine; Hyperalgesia; Neuralgia; Neurotensin; PD 149163; Peripheral Nervous System Diseases; SR 48692; Serotonin Antagonists; Spinal Cord.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

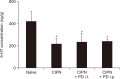
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

