N,N-dimethyltryptamine compound found in the hallucinogenic tea ayahuasca, regulates adult neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 32989216
- PMCID: PMC7522265
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-020-01011-0
N,N-dimethyltryptamine compound found in the hallucinogenic tea ayahuasca, regulates adult neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
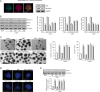
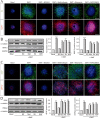
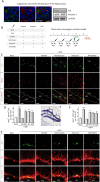
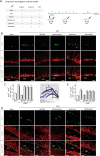
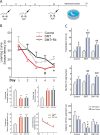
N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a component of the ayahuasca brew traditionally used for ritual and therapeutic purposes across several South American countries. Here, we have examined, in vitro and vivo, the potential neurogenic effect of DMT. Our results demonstrate that DMT administration activates the main adult neurogenic niche, the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, promoting newly generated neurons in the granular zone. Moreover, these mice performed better, compared to control non-treated animals, in memory tests, which suggest a functional relevance for the DMT-induced new production of neurons in the hippocampus. Interestingly, the neurogenic effect of DMT appears to involve signaling via sigma-1 receptor (S1R) activation since S1R antagonist blocked the neurogenic effect. Taken together, our results demonstrate that DMT treatment activates the subgranular neurogenic niche regulating the proliferation of neural stem cells, the migration of neuroblasts, and promoting the generation of new neurons in the hippocampus, therefore enhancing adult neurogenesis and improving spatial learning and memory tasks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

