Primary pulmonary vein stenosis among premature infants with single-vessel disease
- PMID: 32989220
- PMCID: PMC8593792
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-020-00830-9
Primary pulmonary vein stenosis among premature infants with single-vessel disease
Abstract
Objectives: Describe outcomes among preterm infants diagnosed with single-vessel primary pulmonary vein stenosis (PPVS) initially treated using conservative management (active surveillance with deferral of treatment).
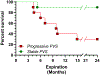
Study design: Retrospective cohort study at a single, tertiary-center (2009-2019) among infants <37 weeks' gestation with single-vessel PPVS. Infants were classified into two categories: disease progression and disease stabilization. Cardiopulmonary outcomes were examined, and a Kaplan-Meier survival analysis performed.
Results: Twenty infants were included. Compared to infants in the stable group (0/10, 0%), all infants in the progressive group had development of at least severe stenosis or atresia (10/10, 100%; P < 0.01). Severe pulmonary hypertension at diagnosis was increased in the progressive (5/10, 50%) versus the stable group (0/10, 0%; P = 0.03). Survival was lower among infants in the progressive than the stable group (log-rank test, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Among preterm infants with single-vessel PPVS, risk stratification may be possible, wherein more targeted, individualized therapies could be applied.
© 2020. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Holt DB, Moller JH, Larson S, Johnson MC. Primary pulmonary vein stenosis. Am J Cardiol 2007, 99(4): 568–572. - PubMed
-
- Bini RM, Cleveland DC, Ceballos R, Bargeron LM Jr., Pacifico AD, Kirklin JW. Congenital pulmonary vein stenosis. Am J Cardiol 1984, 54(3): 369–375. - PubMed
-
- Kalfa D, Belli E, Bacha E, Lambert V, di Carlo D, Kostolny M, et al. Primary Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Outcomes, Risk Factors, and Severity Score in a Multicentric Study. Ann Thorac Surg 2017, 104(1): 182–189. - PubMed
-
- Latson LA, Prieto LR. Congenital and acquired pulmonary vein stenosis. Circulation 2007, 115(1): 103–108. - PubMed
-
- del Cerro MJ, Sabate Rotes A, Carton A, Deiros L, Bret M, Cordeiro M, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical findings, cardiovascular anomalies and outcomes. Pediatr Pulmonol 2014, 49(1): 49–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL136963/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145032/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL145032/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01HL13693/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical