SIRT1 is downregulated by autophagy in senescence and ageing
- PMID: 32989246
- PMCID: PMC7805578
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-020-00579-5
SIRT1 is downregulated by autophagy in senescence and ageing
Abstract
SIRT1 (Sir2) is an NAD+-dependent deacetylase that plays critical roles in a broad range of biological events, including metabolism, the immune response and ageing1-5. Although there is strong interest in stimulating SIRT1 catalytic activity, the homeostasis of SIRT1 at the protein level is poorly understood. Here we report that macroautophagy (hereafter referred to as autophagy), a catabolic membrane trafficking pathway that degrades cellular components through autophagosomes and lysosomes, mediates the downregulation of mammalian SIRT1 protein during senescence and in vivo ageing. In senescence, nuclear SIRT1 is recognized as an autophagy substrate and is subjected to cytoplasmic autophagosome-lysosome degradation, via the autophagy protein LC3. Importantly, the autophagy-lysosome pathway contributes to the loss of SIRT1 during ageing of several tissues related to the immune and haematopoietic system in mice, including the spleen, thymus, and haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, as well as in CD8+CD28- T cells from aged human donors. Our study reveals a mechanism in the regulation of the protein homeostasis of SIRT1 and suggests a potential strategy to stabilize SIRT1 to promote productive ageing.
Figures
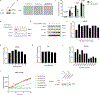




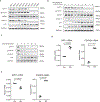

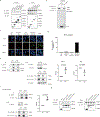

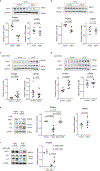
Comment in
-
Autophagy goes nuclear.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Oct;22(10):1159-1161. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-00587-5. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32989248 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lin SJ, Defossez PA & Guarente L. Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for lifespan extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 289, 2126–2128 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Tissenbaum HA & Guarente L. Increased dosage of a sir-2 gene extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 410, 227–230 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM007618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG065500/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 CA115679/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA114046/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG031862/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095675/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG053406/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI083139/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG053406/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133828/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

