Melatonin prevents the binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptor and promotes the expression of extracellular matrix-associated genes in nucleus pulposus cells
- PMID: 32989385
- PMCID: PMC7517348
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9227
Melatonin prevents the binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptor and promotes the expression of extracellular matrix-associated genes in nucleus pulposus cells
Abstract
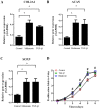
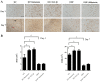
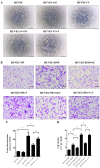
The mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) involve numerous factors, including loss of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and vascular ingrowth. Melatonin has been reported to protect intervertebral discs (IVDs) from degeneration and to exert a potential anti-angiogenic effect. The aim of the present study was to investigate the anti-angiogenic and anabolic effects of melatonin in IVDs. Human nucleus pulposus (NP) and degenerative nucleus pulposus (DNP) cells were isolated and treated with melatonin. The results indicated that melatonin promoted ECM synthesis and NP cell proliferation. In addition, an NP/DNP and human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) co-culture model was used to investigate the anti-angiogenesis effect of melatonin. Melatonin was indicated to suppress tube formation and migration of HUVECs in culture with NP cell-conditioned medium, as well as in an NP cell co-culture model. Fluorescence-labeled vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was used to study the binding between VEGF and its receptor. The results of the present study indicated that melatonin exerts an angiogenic effect via inhibition of the binding of VEGF to its receptor in HUVECs. Taken together, these results suggest that melatonin is a potential agent to prevent IDD.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; intervertebral disc degeneration; melatonin; nucleus pulposus.
Copyright: © Shen et al.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
