A Narrative Review on Clinical Applications of fNIRS
- PMID: 32989620
- PMCID: PMC7573058
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-020-00387-1
A Narrative Review on Clinical Applications of fNIRS
Abstract
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is a relatively new imaging modality in the functional neuroimaging research arena. The fNIRS modality non-invasively investigates the change of blood oxygenation level in the human brain utilizing the transillumination technique. In the last two decades, the interest in this modality is gradually evolving for its real-time monitoring, relatively low-cost, radiation-less environment, portability, patient-friendliness, etc. Including brain-computer interface and functional neuroimaging research, this technique has some important application of clinical perspectives such as Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, dyslexia, Parkinson's disease, childhood disorders, post-neurosurgery dysfunction, attention, functional connectivity, and many more can be diagnosed as well as in some form of assistive modality in clinical approaches. Regarding the issue, this review article presents the current scopes of fNIRS in medical assistance, clinical decision making, and future perspectives. This article also covers a short history of fNIRS, fundamental theories, and significant outcomes reported by a number of scholarly articles. Since this review article is hopefully the first one that comprehensively explores the potential scopes of the fNIRS in a clinical perspective, we hope it will be helpful for the researchers, physicians, practitioners, current students of the functional neuroimaging field, and the related personnel for their further studies and applications.
Keywords: Anesthetic depth monitoring; Assistive modality; Behavioral disorder; Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS); Neurological disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
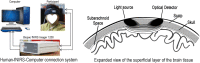
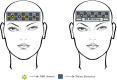







References
-
- Brazy JE, Lewis DV, Mitnick MH, Jöbsis vander Vliet FF. Noninvasive monitoring of cerebral oxygenation in preterm infants: preliminary observations. Pediatrics. 1985;75:217–225. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari M, Giannini I, Carpi A, Fasella P, Fieschi C, Zanette E: Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of tissue oxygenation and circulatory parameters. XII World Congress of Angiology, Athens, September 7–12, abs. 663, 1980
-
- Wolf M, Naulaers G, van Bel F, Kleiser S, Greisen G: A review of near-infrared spectroscopy for term and preterm newborns. J Near Infrared Spectrosc. 20, 2012. 10.1255/jnirs.972
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

