Integrative genomic analysis in African American children with asthma finds three novel loci associated with lung function
- PMID: 32989782
- PMCID: PMC7902343
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.22365
Integrative genomic analysis in African American children with asthma finds three novel loci associated with lung function
Abstract
Bronchodilator (BD) drugs are commonly prescribed for treatment and management of obstructive lung function present with diseases such as asthma. Administration of BD medication can partially or fully restore lung function as measured by pulmonary function tests. The genetics of baseline lung function measures taken before BD medication have been extensively studied, and the genetics of the BD response itself have received some attention. However, few studies have focused on the genetics of post-BD lung function. To address this gap, we analyzed lung function phenotypes in 1103 subjects from the Study of African Americans, Asthma, Genes, and Environment, a pediatric asthma case-control cohort, using an integrative genomic analysis approach that combined genotype, locus-specific genetic ancestry, and functional annotation information. We integrated genome-wide association study (GWAS) results with an admixture mapping scan of three pulmonary function tests (forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1 ], forced vital capacity [FVC], and FEV1 /FVC) taken before and after albuterol BD administration on the same subjects, yielding six traits. We identified 18 GWAS loci, and five additional loci from admixture mapping, spanning several known and novel lung function candidate genes. Most loci identified via admixture mapping exhibited wide variation in minor allele frequency across genotyped global populations. Functional fine-mapping revealed an enrichment of epigenetic annotations from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, fetal lung tissue, and lung fibroblasts. Our results point to three novel potential genetic drivers of pre- and post-BD lung function: ADAMTS1, RAD54B, and EGLN3.
Keywords: African American; GWAS; admixture; asthma; integrative genomic analysis; lung function.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures


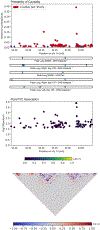
References
-
- Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America. (2019). Asthma diagnosis. https://www.aafa.org/lung-function-tests-diagnose-asthma/
-
- Astle WJ, Elding H, Jiang T, Allen D, Ruklisa D, Mann AL, Mead D, Bouman H, Riveros-Mckay F, Kostadima MA, Lambourne JJ, Sivapalaratnam S, Downes K, Kundu K, Bomba L, Berentsen K, Bradley JR, Daugherty LC, Delaneau O, … Soranzo N (2016). The allelic landscape of human blood cell trait variation and links to common complex disease. Cell, 167(5), 1415–1429e19. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG007419/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113003/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141845/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133433/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL104608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009080/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES024844/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K22 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MD013312/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 GM118985/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- TL4 GM118986/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T34 GM008574/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL138626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141992/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL140218/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 GM081266/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD085993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007546/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD006902/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- RL5 GM118984/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD010443/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States

