Inaccurate Use of the Upper Extremity Fugl-Meyer Negatively Affects Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Trial Design: Findings From the ICARE Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32991872
- PMCID: PMC7854957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2020.08.019
Inaccurate Use of the Upper Extremity Fugl-Meyer Negatively Affects Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Trial Design: Findings From the ICARE Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: To determine the extent to which estimates of sample and effect size in stroke rehabilitation trials can be affected by simple summation of ordinal Upper Extremity Fugl-Meyer (UEFM) items compared with a Rasch-rescaled UEFM.
Design: Rasch analysis of Interdisciplinary Comprehensive Arm Rehabilitation Evaluation (ICARE) phase III trial data, comparing 3 upper extremity (UE) motor treatments in stroke survivors enrolled 45.8±22.4 days poststroke. Participants underwent a structured UE motor training known as the Accelerated Skill Acquisition Program, usual and customary care, or dose-equivalent care. UEFM data from baseline, postintervention, and 6 and 12 months later were included for analysis.
Setting: Outpatient stroke rehabilitation.
Participants: ICARE participants (N=361).
Interventions: Not applicable.
Main outcome measures: Item difficulties, person abilities, and sample size.
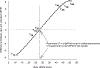
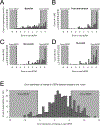
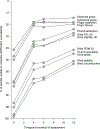
Results: Because of their ordinality, summed raw UEFM scores measured motor impairment inconsistently across different ranges of stroke severity relative to the rescaled UEFM. In the full ICARE sample, raw UEFM understated scores relative to the rescaled UEFM by 7.4 points for the most severely impaired, but overstated scores by up to 8.4 points toward the ceiling. As a result, 50.9% of all UEFM observations showed a residual error greater than 10% of the total UEFM score. Relative to the raw scores, the rescaled UEFM improved the effect size of change in motor impairment between baseline and 1 year (d=0.35). For a hypothetical 3-arm trial resembling ICARE, UEFM rescaling reduced the required sample size by 32% (n=108) compared with raw UEFM (n=159).
Conclusions: In UE rehabilitation trials, a rescaled UEFM potentially decreases sample size by one-third, decreasing costs, duration, and the number of subjects exposed to experimental risks. This benefit is obtained through increased measurement efficiency. Reductions in ceiling effects are also possible. These findings apply to ICARE-like trials. Confirmatory validation in another phase III trial is needed.
Keywords: Clinical trials as topic; Data accuracy; Disability evaluation; Recovery of function; Rehabilitation; Sample size; Stroke; Stroke rehabilitation; Upper extremity.
Copyright © 2020 American Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Localio AR, Stack CB, Meibohm AR, et al. Inappropriate Statistical Analysis and Reporting in Medical Research: Perverse Incentives and Institutional SolutionsInappropriate Statistical Analysis and Reporting in Medical Research. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2018;169(8):577–578. - PubMed
-
- Fugl-Meyer AR, Jaasko L, Leyman I, Olsson S, Steglind S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. a method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1975;7(1):13–31. - PubMed
-
- van Wijck FM, Pandyan AD, Johnson GR, Barnes MP. Assessing motor deficits in neurological rehabilitation: patterns of instrument usage. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2001;15(1):23–30. - PubMed
-
- Woodbury ML, Velozo CA, Richards LG, Duncan PW, Studenski S, Lai S-M. Dimensionality and construct validity of the Fugl-Meyer Assessment of the upper extremity. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2007;88(6):715–723. - PubMed
-
- Woodbury ML, Velozo CA, Richards LG, Duncan PW. Rasch analysis staging methodology to classify upper extremity movement impairment after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;94(8):1527–1533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

