On-demand degradable embolic microspheres for immediate restoration of blood flow during image-guided embolization procedures
- PMID: 32992115
- PMCID: PMC7673262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120408
On-demand degradable embolic microspheres for immediate restoration of blood flow during image-guided embolization procedures
Abstract
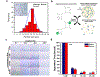
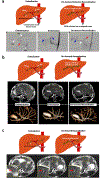
Degradable embolic agents that provide transient arterial occlusion during embolization procedures have been of interest for many years. Ideally, embolic agents are visible with standard imaging modalities and offer on-demand degradability, permitting physicians to achieve desired arterial occlusion tailored to patient and procedure indication. Subsequent arterial recanalization potentially enhances the overall safety and efficacy of embolization procedures. Here, we report on-demand degradable and MRI-visible microspheres for embolotherapy. Embolic microspheres composed of calcium alginate and USPIO nanoclusters were synthesized with an air spray atomization and coagulation reservoir equipped with a vacuum suction. An optimized distance between spray nozzle and reservoir allowed uniform size and narrow size distribution of microspheres. The fabricated alginate embolic microspheres crosslinked with Ca2+ demonstrated highly responsive on-demand degradation properties in vitro and in vivo. Finally, the feasibility of using the microspheres for clinical embolization and recanalization procedures was evaluated with interventional radiologists in rabbits. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) guided embolization of hepatic arteries with these embolic microspheres was successfully performed and the occlusion of artery was confirmed with DSA images and contrast enhanced MRI. T2 MRI visibility of the microspheres allowed to monitor the distribution of intra-arterial (IA) infused embolic microspheres. Subsequent on-demand image-guided recanalization procedures were also successfully performed with rapid degradation of microspheres upon intra-arterial infusion of an ion chelating agent. These instant degradable embolic microspheres will permit effective on-demand embolization/recanalization procedures offering great promise to overcome limitations of currently available permanent and biodegradable embolic agents.
Keywords: Embolic agents; Embolization; Embolotherapy; Interventional radiology; On-demand degradable microspheres.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Jander HP, Russinovich NA, Transcatheter gelfoam embolization in abdominal, retroperitoneal, and pelvic hemorrhage, Radiology 136 (2) (1980) 337–344. - PubMed
-
- DeHoll J, Shin P, Angle J, Steers W, Alternative approaches to the management of priapism, Int. J. Impot. Res. 10 (1) (1998) 11–14. - PubMed
-
- Peck DJ, McLoughlin RF, Hughson MN, Rankin RN, Percutaneous embolotherapy of lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, J. Vasc. Intervent. Radiol. 9 (5) (1998) 747–751. - PubMed
-
- Lin D-Y, Liaw Y-F, Lee T-Y, Lai C-M, Hepatic arterial embolization in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma—a randomized controlled trial, Gastroenterology 94 (2) (1988) 453–456. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein HM, Medellin H, Beydoun MT, Wallace S, Ben-Menachem Y, Bracken R, Johnson DE, Transcatheter embolization of renal cell carcinoma, Am. J. Roentgenol. 123 (3) (1975) 557–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

