Binding Mechanism Elucidation of the Acute Respiratory Disease Causing Agent Adenovirus of Serotype 7 to Desmoglein-2
- PMID: 32992715
- PMCID: PMC7599583
- DOI: 10.3390/v12101075
Binding Mechanism Elucidation of the Acute Respiratory Disease Causing Agent Adenovirus of Serotype 7 to Desmoglein-2
Abstract
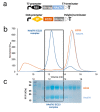
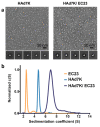
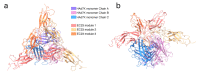
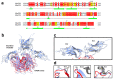
The study of viruses causing acute respiratory distress syndromes (ARDS) is more essential than ever at a time when a virus can create a global pandemic in a matter of weeks. Among human adenoviruses, adenovirus of serotype 7 (HAdV7) is one of the most virulent serotypes. This virus regularly re-emerges in Asia and has just been the cause of several deaths in the United States. A critical step of the virus life cycle is the attachment of the knob domain of the fiber (HAd7K) to the cellular receptor desmoglein-2 (DSG2). Complexes between the fiber knob and two extracellular domains of DSG2 have been produced. Their characterization by biochemical and biophysical methods show that these two domains are sufficient for the interaction and that the trimeric HAd7K could accommodate up to three DSG2 receptor molecules. The cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of these complexes at 3.1 Å resolution confirmed the biochemical data, and allowed the identification of the critical amino acid residues for this interaction, which shows similarities with other DSG2 interacting adenoviruses, despite a low homology in the primary sequences.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndromes; adenoviruses; cryo-electron microscopy; desmoglein-2; virus-host interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Human Adenovirus Working Group. [(accessed on 23 April 2020)]; Available online: http://hadvwg.gmu.edu/
-
- Kim Y.-J., Hong J.-Y., Lee H.-J., Shin S.-H., Kim Y.K., Inada T., Hashido M., Piedra P.A. Genome Type Analysis of Adenovirus Types 3 and 7 Isolated during Successive Outbreaks of Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003;41:4594–4599. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4594-4599.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

