A Magnetoelectric Automotive Crankshaft Position Sensor
- PMID: 32992763
- PMCID: PMC7582794
- DOI: 10.3390/s20195494
A Magnetoelectric Automotive Crankshaft Position Sensor
Abstract
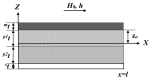
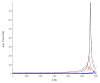
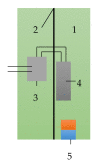
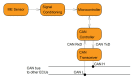
The paper is devoted to the possibility of using magnetoelectric materials for the production of a crankshaft position sensor for automobiles. The composite structure, consisting of a PZT or LiNbO3 piezoelectric with a size of 20 mm × 5 mm × 0.5 mm, and plates of the magnetostrictive material Metglas of the appropriate size were used as a sensitive element. The layered structure was made from a bidomain lithium niobate monocrystal with a Y + 128° cut and amorphous metal of Metglas. Various combinations of composite structures are also investigated; for example, asymmetric structures using a layer of copper and aluminum. The output characteristics of these structures are compared in the resonant and non-resonant modes. It is shown that the value of the magnetoelectric resonant voltage coefficient was 784 V/(cm·Oe), and the low-frequency non-resonant magnetoelectric coefficient for the magnetoelectric element was about 3 V/(cm·Oe). The principle of operation of the position sensor and the possibility of integration into automotive systems, using the CAN bus, are examined in detail. To obtain reliable experimental results, a special stand was assembled on the basis of the SKAD-1 installation. The studies showed good results and a high prospect for the use of magnetoelectric sensors as position sensors and, in particular, of a vehicle's crankshaft position sensor.
Keywords: automotive sensor; crankshaft position sensor; magnetoelectric effect; magnetoelectric sensor; magnetoelectric structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Palneedi H., Annapureddy V., Priya S., Ryu J. Status and perspectives of multiferroic magnetoelectric composite materials and applications. Actuators. 2016;5:9. doi: 10.3390/act5010009. - DOI
-
- Myers R., Islam R.A., Karmarkar M., Priya S. Magnetoelectric laminate composite based tachometer for harsh environment applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007;91:122904. doi: 10.1063/1.2784959. - DOI
-
- Yang B., Yang Y. A new angular velocity sensor with ultrahigh resolution using magnetoelectric effect under the principle of Coriolis force. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016;238:234–239. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2015.12.021. - DOI
-
- Wu Z., Bian L., Wang S., Zhang X. An angle sensor based on magnetoelectric effect. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017;262:108–113. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2017.04.049. - DOI
-
- Shi Z., Huang Q., Wu G.S., Xu Y.-H., Yang M., Liu X.-J., Wang C.P., Ma J. Design and Development of a Tachometer Using Magnetoelectric Composite as Magnetic Field Sensor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017;54:1–4. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2017.2721900. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

