Spectroscopic Properties of Two 5'-(4-Dimethylamino)Azobenzene Conjugated G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides
- PMID: 32993097
- PMCID: PMC7582650
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197103
Spectroscopic Properties of Two 5'-(4-Dimethylamino)Azobenzene Conjugated G-Quadruplex Forming Oligonucleotides
Abstract
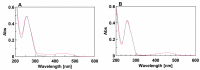
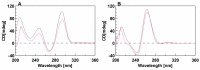
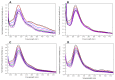
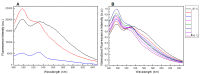
The synthesis of two 5'-end (4-dimethylamino)azobenzene conjugated G-quadruplex forming aptamers, the thrombin binding aptamer (TBA) and the HIV-1 integrase aptamer (T30695), was performed. Their structural behavior was investigated by means of UV, CD, fluorescence spectroscopy, and gel electrophoresis techniques in K+-containing buffers and water-ethanol blends. Particularly, we observed that the presence of the 5'-(4-dimethylamino)azobenzene moiety leads TBA to form multimers instead of the typical monomolecular chair-like G-quadruplex and almost hampers T30695 G-quadruplex monomers to dimerize. Fluorescence studies evidenced that both the conjugated G-quadruplexes possess unique fluorescence features when excited at wavelengths corresponding to the UV absorption of the conjugated moiety. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of the trans-cis conversion of the dye incorporated at the 5'-end of TBA and T30695 showed that, unlike the free dye, in K+-containing water-ethanol-triethylamine blend the trans-to-cis conversion was almost undetectable by means of a standard UV spectrophotometer.
Keywords: 5′-(4-dimethylamino)azobenzene phosphoramidite derivative; CD G-quadruplexes; G-quadruplexes; azobenzenes; conjugated aptamers; fluorescence G-quadruplexes; trans-cis conversion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Oikonomidi I., Burbridge E., Cavadas M., Sullivan G., Clancy D., Collis B., Březinová .J., Humpolickova J., Hu T., Bileck A., et al. Structural Features of Nucleoprotein CST/Shelterin Complex Involved in the Telomere Maintenance and Its Association with Disease Mutations. Cells 2020. Volume 9. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA: 2018. iTAP, a novel iRhom interactor, controls TNF secretion by policing the stability of iRhom/TACE; p. e35032. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

