Transcriptome analysis reveals underlying immune response mechanism of fungal (Penicillium oxalicum) disease in Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. chow (Orchidaceae)
- PMID: 32993485
- PMCID: PMC7525978
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-020-02653-4
Transcriptome analysis reveals underlying immune response mechanism of fungal (Penicillium oxalicum) disease in Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. chow (Orchidaceae)
Abstract
Background: Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. Chow is a medicinal plant. G. elata f. glauca is unavoidably infected by pathogens in their growth process. In previous work, we have successfully isolated and identified Penicillium oxalicum from fungal diseased tubers of G. elata f. glauca. As a widespread epidemic, this fungal disease seriously affected the yield and quality of G. elata f. glauca. We speculate that the healthy G. elata F. glauca might carry resistance genes, which can resist against fungal disease. In this study, healthy and fungal diseased mature tubers of G. elata f. glauca from Changbai Mountain area were used as experimental materials to help us find potential resistance genes against the fungal disease.
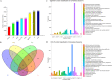
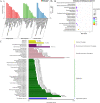
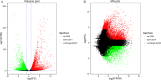
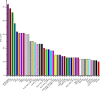
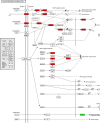
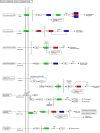
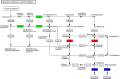
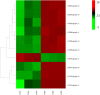
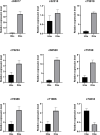
Results: A total of 7540 differentially expressed Unigenes (DEGs) were identified (FDR < 0.01, log2FC > 2). The current study screened 10 potential resistance genes. They were attached to transcription factors (TFs) in plant hormone signal transduction pathway and plant pathogen interaction pathway, including WRKY22, GH3, TIFY/JAZ, ERF1, WRKY33, TGA. In addition, four of these genes were closely related to jasmonic acid signaling pathway.
Conclusions: The immune response mechanism of fungal disease in G. elata f. glauca is a complex biological process, involving plant hormones such as ethylene, jasmonic acid, salicylic acid and disease-resistant transcription factors such as WRKY, TGA.
Keywords: Changbai Mountain area; Fungal disease; immune response; Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. chow; Orchidaceae; Transcription factors; Transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of seed germinating fungi (Mycetinis scorodonius) from Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. chow in Changbai Mountain and examination of their germination ability.Sci Rep. 2024 May 28;14(1):12215. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63189-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38806667 Free PMC article.
-
An exploration of mechanism of high quality and yield of Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca by the isolation, identification and evaluation of Armillaria.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Dec 30;22(1):621. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-04007-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36581798 Free PMC article.
-
An exploration of mechanism of high quality and yield of Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca by the isolation, identification, and evaluation of Mycena.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1220670. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1220670. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37928654 Free PMC article.
-
The rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume - An ethnopharmacological review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:361-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.057. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27377337 Review.
-
A Review of Gastrodia Elata Bl.: Extraction, Analysis and Application of Functional Food.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024 Sep 27:1-30. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2024.2397994. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39355975 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of the fully mycoheterotrophic orchid Gastrodia elata.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Mar 4;12(3):jkab433. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab433. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35100375 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Ribosomal Protein GhRPS6 and Its Role in Cotton Verticillium Wilt Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1795. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041795. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670294 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of seed germinating fungi (Mycetinis scorodonius) from Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. chow in Changbai Mountain and examination of their germination ability.Sci Rep. 2024 May 28;14(1):12215. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63189-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38806667 Free PMC article.
-
Cytological and transcriptomic analysis to unveil the mechanism of web blotch resistance in Peanut.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Oct 26;23(1):518. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04545-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37884908 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of resistant and susceptible Kentucky bluegrass varieties in response to powdery mildew infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Nov 2;22(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03883-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36319971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2020. p. 59.
-
- Lin YE, Chou ST, Lin SH, Lu KH, Panyod S, Lai YS, Ho CT, Sheen LY. Antidepressant-like effects of water extract of Gastrodia elata Blume on neurotrophic regulation in a chronic social defeat stress model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;215:132–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

