Mammographic density change in a cohort of premenopausal women receiving tamoxifen for breast cancer prevention over 5 years
- PMID: 32993747
- PMCID: PMC7523310
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-020-01340-4
Mammographic density change in a cohort of premenopausal women receiving tamoxifen for breast cancer prevention over 5 years
Abstract
Background: A decrease in breast density due to tamoxifen preventive therapy might indicate greater benefit from the drug. It is not known whether mammographic density continues to decline after 1 year of therapy, or whether measures of breast density change are sufficiently stable for personalised recommendations.
Methods: Mammographic density was measured annually over up to 5 years in premenopausal women with no previous diagnosis of breast cancer but at increased risk of breast cancer attending a family-history clinic in Manchester, UK (baseline 2010-2013). Tamoxifen (20 mg/day) for prevention was prescribed for up to 5 years in one group; the other group did not receive tamoxifen and were matched by age. Fully automatic methods were used on mammograms over the 5-year follow-up: three area-based measures (NN-VAS, Stratus, Densitas) and one volumetric (Volpara). Additionally, percentage breast density at baseline and first follow-up mammograms was measured visually. The size of density declines at the first follow-up mammogram and thereafter was estimated using a linear mixed model adjusted for age and body mass index. The stability of density change at 1 year was assessed by evaluating mean squared error loss from predictions based on individual or mean density change at 1 year.
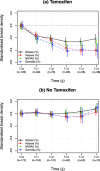
Results: Analysis used mammograms from 126 healthy premenopausal women before and as they received tamoxifen for prevention (median age 42 years) and 172 matched controls (median age 41 years), with median 3 years follow-up. There was a strong correlation between percentage density measures used on the same mammogram in both the tamoxifen and no tamoxifen groups (all correlation coeficients > 0.8). Tamoxifen reduced mean breast density in year 1 by approximately 17-25% of the inter-quartile range of four automated percentage density measures at baseline, and from year 2, it decreased further by approximately 2-7% per year. Predicting change at 2 years using individual change at 1 year was approximately 60-300% worse than using mean change at 1year.
Conclusions: All measures showed a consistent and large average tamoxifen-induced change in density over the first year, and a continued decline thereafter. However, these measures of density change at 1 year were not stable on an individual basis.
Keywords: Breast density change; Mammographic density; Prevention; Tamoxifen.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof Evans and Howell report receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca. Prof Cuzick has received funding from Sanofi-Aventis and AstraZeneca, and is a paid member of a speaker’s bureau for AstraZeneca. Prof Cuzick and Dr Brentnall report receiving royalty payments through Cancer Research UK for commercial use of the Tyrer–Cuzick algorithm to assess breast cancer risk. None of the other authors report any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rugo HS, Rumble RB, Macrae E, Barton DL, Connolly HK, Dickler MN, Fallowfield L, Fowble B, Ingle JN, Jahanzeb M, Johnston SRD, Korde LA, Khatcheressian JL, Mehta RS, Muss HB, Burstein HJ. Endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(25):3069–103. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Clarke M, Cutter D, Darby S, McGale P, Pan HC, Taylor C, Wang YC, Dowsett M, Ingle J, Peto R. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9793):771–84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Bonanni B, Costantino JP, Cummings S, DeCensi A, Dowsett M, Forbes JF, Ford L, LaCroix AZ, Mershon J, Mitlak BH, Powles T, Veronesi U, Vogel V, Wickerham DL, SERM Chemoprevention of Breast Cancer Overview Group Selective oestrogen receptor modulators in prevention of breast cancer: an updated meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet. 2013;381(9880):1827–34. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

