Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter (MCU) deficiency reveals an alternate path for Ca2+ uptake in photoreceptor mitochondria
- PMID: 32994451
- PMCID: PMC7525533
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72708-x
Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter (MCU) deficiency reveals an alternate path for Ca2+ uptake in photoreceptor mitochondria
Abstract
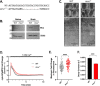
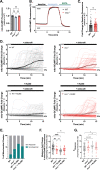
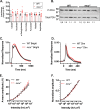
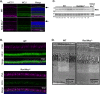
Rods and cones use intracellular Ca2+ to regulate many functions, including phototransduction and neurotransmission. The Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter (MCU) complex is thought to be the primary pathway for Ca2+ entry into mitochondria in eukaryotes. We investigate the hypothesis that mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake via MCU influences phototransduction and energy metabolism in photoreceptors using a mcu-/- zebrafish and a rod photoreceptor-specific Mcu-/- mouse. Using genetically encoded Ca2+ sensors to directly examine Ca2+ uptake in zebrafish cone mitochondria, we found that loss of MCU reduces but does not eliminate mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. Loss of MCU does not lead to photoreceptor degeneration, mildly affects mitochondrial metabolism, and does not alter physiological responses to light, even in the absence of the Na+/Ca2+, K+ exchanger. Our results reveal that MCU is dispensable for vertebrate photoreceptor function, consistent with its low expression and the presence of an alternative pathway for Ca2+ uptake into photoreceptor mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests (financial and/or non-financial), or other interests which might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion of this paper.
Figures
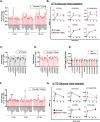
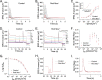
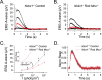
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EY006641/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 EY006641/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY002687/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY026020/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY026020/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY027387/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY027387/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F31EY031165/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY028645/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY06641/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- EY026675/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R00 EY026651/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 EY031165/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY026651/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY017863/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030912/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 EY026651/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

