Tympano-Mastoid Cholesterol Granuloma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 32994699
- PMCID: PMC7502992
- DOI: 10.1177/1179547620958728
Tympano-Mastoid Cholesterol Granuloma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
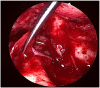
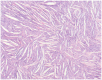
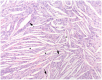
Cholesterol granuloma (CG) is a rare condition histological consisting of a foreign body, giant cell reaction to cholesterol crystals and haemosiderin derived from the ruptured of the erythrocytes. A 25-year-old man came to our Department presenting signs and symptoms of tympano-mastoid cholesterol granuloma. He showed all the specific sign and symptoms of the disease. However, considering the lack of literature regarding TMCG, this study was performed with the aim of presenting the main characteristics of tympano-mastoid CG, describing the case report and reviewing the literature.
Keywords: Cholesterol granuloma; cholesterol crystal; mastoid; middle ear; review.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting Interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Campos A, Armengot M, Zapater E, Hostalet F, Basterra J. Cholesterol granuloma of the middle ear: report of 5 cases. Acta Otolaryngol. 1996; 50:125-129. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

