APOE2 promotes the development and progression of subretinal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration via MAPKs signaling pathway
- PMID: 32994736
- PMCID: PMC7499293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.06.037
APOE2 promotes the development and progression of subretinal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration via MAPKs signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nvAMD) is one of the main pathological features of wet AMD. Apolipoprotein E2 is involved in the formation of nvAMD but the molecular mechanism has not been reported.
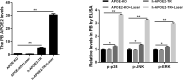
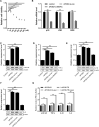
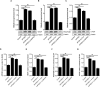
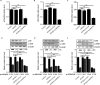
Methods: The APOE alleles in AMD patients were detected by genotyping. Mouse models were divided into 4 groups according to transfection different gene segments and laser-induced treatment. APOE2, VEGF, PDGF-BB, b-FGF and inflammatory cytokines (including p-NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) were tested by ELISA in mice retinal lysate. The formation of nvAMD in the indicated treatment groups at 3rd, 7th and 14th day after laser-induced damage were detected by FFA. Besides, qRT-PCR was used to determine the mRNA levels of p38, JNK and ERK in ARPE-19 cells. Finally, the inflammatory cytokines and MAPK proteins (including P38, p-P38, JNK, p-JNK, ERK and p-ERK) were detected by western blot.
Results: The statistics of APOE alleles showed that APOE2 allele carriers were more likely to nvAMD. VEGF, PDGF-BB, b-FGF and related inflammatory cytokines were up-regulated significantly after treatment with APOE2, which were reduced after silencing the MAPK family genes, however. Further, the expression levels of neovascular growth factors and inflammatory cytokines were highly consistent between mouse models and ARPE-19 cells. Besides, the phosphorylation levels of p38, JNK and ERK were affected by APOE2.
Conclusion: nvAMD was affected directly by the overexpression of VEGF, PDGF-BB and b-FGF, which were regulated by APOE2 through activating MAPKs pathway.
Keywords: APOE2; Inflammatory cytokines; MAPKs pathway; nvAMD.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors hereby agreed and confirm that there is no conflict of interest for this research work and publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Blasiak, Salminen, Kaarniranta Potential of epigenetic mechanisms in AMD pathology. Front. Biosci. 2013;5:412–425. - PubMed
-
- Busch, WasmuthSpital, Lommatzsch Activation of the ERK1/2-MAPK signaling pathway by complement serum in UV-POS-pretreated ARPE-19 cells. Ophthalmologica. J. Int. d'ophtalmologie. Int. J. Ophthalmol. Z. Augenheilkunde. 2018;239(4):215–224. - PubMed
-
- Feng, Kong, Wang, He The protective effect of coptisine on experimental atherosclerosis ApoE(-/-) mice is mediated by MAPK/NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Biomed. Pharmacotherapy = Biomed. Pharmacotherapie. 2017;93:721–729. - PubMed
-
- Goverdhan, Thomson, Lotery, 2013. Animal models of age-related macular degeneration. Drug Discov. Today: Dis. Models 10(4).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

