Pathogenesis of psoriasis in the "omic" era. Part III. Metabolic disorders, metabolomics, nutrigenomics in psoriasis
- PMID: 32994764
- PMCID: PMC7507147
- DOI: 10.5114/ada.2020.98284
Pathogenesis of psoriasis in the "omic" era. Part III. Metabolic disorders, metabolomics, nutrigenomics in psoriasis
Abstract
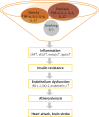
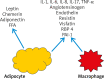
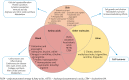
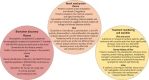
Psoriasis is a systemic disease that is strictly connected with metabolic disorders (insulin resistance, atherogenic dyslipidemia, arterial hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases). It occurs more often in patients with a more severe course of the disease. Obesity is specially an independent risk factor and it is associated with a worse treatment outcome because of the high inflammatory activity of visceral fatty tissue and the production of inflammatory mediators involved in the development of both psoriasis and metabolic disorders. However, in psoriasis the activation of the Th17/IL-17 and the abnormalities in the Th17/Treg balance axis are observed, but this pathomechanism does not fully explain the frequent occurrence of metabolic disorders. Therefore, there is a need to look for better biomarkers in the diagnosis, prognosis and monitoring of concomitant disorders and therapeutic effects in psoriasis. In addition, the education on the use of a proper diet as a prophylaxis for the development of the above disorders is an important element of holistic care for a patient with psoriasis. Diet may affect gene expression due to epigenetic modification which encompasses interactions of environment, nutrition and diseases. Patients with psoriasis should be advised to adopt proper diet and dietician support.
Keywords: inflammation; metabolic syndrome; metabolomics; proteomic nutrigenomics; psoriasis.
Copyright: © 2020 Termedia Sp. z o. o.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Deng Y, Chang C, Lu Q. The inflammatory response in psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;50:377–89. - PubMed
-
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek A, Placek W. Interleukin-17 as a factor linking the pathogenesis of psoriasis with metabolic disorders. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:260–8. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KGMM, Zimmet P, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome – a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
