Artificial intelligence (AI) and big data in cancer and precision oncology
- PMID: 32994889
- PMCID: PMC7490765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.08.019
Artificial intelligence (AI) and big data in cancer and precision oncology
Abstract
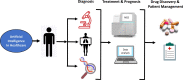
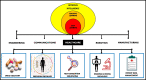
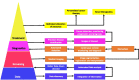
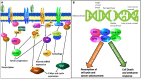
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have significantly influenced many facets of the healthcare sector. Advancement in technology has paved the way for analysis of big datasets in a cost- and time-effective manner. Clinical oncology and research are reaping the benefits of AI. The burden of cancer is a global phenomenon. Efforts to reduce mortality rates requires early diagnosis for effective therapeutic interventions. However, metastatic and recurrent cancers evolve and acquire drug resistance. It is imperative to detect novel biomarkers that induce drug resistance and identify therapeutic targets to enhance treatment regimes. The introduction of the next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms address these demands, has revolutionised the future of precision oncology. NGS offers several clinical applications that are important for risk predictor, early detection of disease, diagnosis by sequencing and medical imaging, accurate prognosis, biomarker identification and identification of therapeutic targets for novel drug discovery. NGS generates large datasets that demand specialised bioinformatics resources to analyse the data that is relevant and clinically significant. Through these applications of AI, cancer diagnostics and prognostic prediction are enhanced with NGS and medical imaging that delivers high resolution images. Regardless of the improvements in technology, AI has some challenges and limitations, and the clinical application of NGS remains to be validated. By continuing to enhance the progression of innovation and technology, the future of AI and precision oncology show great promise.
Keywords: AI, Artificial Intelligence; Artificial intelligence; Big datasets; CNV, Copy Number Variations; Deep learning; Diagnosis; Digital pathology; FFPE, Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded; LYNA, LYmph Node Assistant; ML, Machine Learning; Machine learning; Medical imaging; NGS and bioinformatics; NGS, Next Generation Sequencing; Precision oncology; Prognosis and drug discovery; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; Treatment; WSI, Whole Slide Imaging.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Joshi A.V. Springer Nature Switzerland; 2020. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
