Optimization of green biosynthesized visible light active CuO/ZnO nano-photocatalysts for the degradation of organic methylene blue dye
- PMID: 32995606
- PMCID: PMC7511830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04896
Optimization of green biosynthesized visible light active CuO/ZnO nano-photocatalysts for the degradation of organic methylene blue dye
Abstract
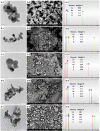
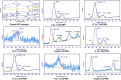
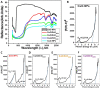
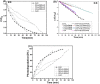
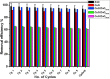
Herein, CuO/ZnO nanocomposites at different ratios were successfully synthesized through a green biosynthesis approach. This was performed by harnessing the fungal-secreted enzymes and proteins during the sol-gel process for nanocomposites seed growth. All fabricated nanoparticles/nanocomposites were characterized using Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FT-IR) Spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM-EDX) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) analyses. The photocatalytic degradation efficacy of the synthesized nanocomposites was evaluated using a cationic methylene blue (MB) dye as a model of reaction. Results obtained from the FT-IR and EDX analyses revealed that CuO-NPs, ZnO-NPs, CuO/ZnO50/50, CuO/ZnO80/20, and CuO/ZnO20/80 were successfully prepared by harnessing the biomass filtrate of Penicillium corylophilum As-1. Furthermore, XRD and TEM revealed the variation in the particle size of the nanocomposites (10-55 nm) with the ratio of the nanoparticles. Notably, the size of the nanocomposites was proportionally increased with an increasing ratio of ZnO-NPs. XPS analysis affirmed the presence of both Cu and Zn in the nanocomposites with varying binding energies compared with individual nanoparticles. Furthermore, a high photo-degradation efficacy was achieved by increasing the ratio of ZnO-NPs in the nanocomposite formulation, and 97% of organic MB dye was removed after 85 min of irradiation using the CuO/ZnO20/80 nanocomposite.
Keywords: Biosynthesis; CuO; Materials chemistry; Materials science; Nanocomposites; Nanotechnology; Penicillium corylophilum; Photocatalyst; ZnO.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures





References
-
- Maity S., Sinha D., Sarkar A. Wastewater and industrial effluent treatment by using nanotechnology. In: Bhushan I., Singh V.K., Tripathi D.K., editors. Nanomaterials and Environmental Biotechnology. Springer International Publishing; Cham: 2020. pp. 299–313.
-
- Hamza M.F., Ahmed F.Y., El-Aassy I., Fouda A., Guibal E. Groundwater purification in a polymetallic mining area (SW Sinai, Egypt) using functionalized magnetic chitosan particles. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018;229:360.
-
- Yogalakshmi K.N., Das A., Rani G., Jaswal V., Randhawa J.S. Nano-bioremediation: a new age technology for the treatment of dyes in textile effluents. Biorem. Ind. Waste Environ. Saf. Springer. 2020:313–347.
-
- Sakib A.A.M., Masum S.M., Hoinkis J., Islam R., Molla M., Islam A. Synthesis of CuO/ZnO nanocomposites and their application in photodegradation of toxic textile dye. J. Compos. Sci. 2019;3:91.
-
- Salem S.S., Mohamed A., El-Gamal M., Talat M., Fouda A. Biological decolorization and degradation of azo dyes from textile wastewater effluent by Aspergillus niger. Egypt. J. Chem. 2019;62:1799–1813.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

