This is a preprint.
Defining the Syrian hamster as a highly susceptible preclinical model for SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 32995767
- PMCID: PMC7523093
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.09.25.314070
Defining the Syrian hamster as a highly susceptible preclinical model for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Update in
-
Defining the Syrian hamster as a highly susceptible preclinical model for SARS-CoV-2 infection.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):2673-2684. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1858177. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 33251966 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Following emergence in late 2019, SARS-CoV-2 rapidly became pandemic and is presently responsible for millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide. There is currently no approved vaccine to halt the spread of SARS-CoV-2 and only very few treatment options are available to manage COVID-19 patients. For development of preclinical countermeasures, reliable and well-characterized small animal disease models will be of paramount importance. Here we show that intranasal inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 into Syrian hamsters consistently caused moderate broncho-interstitial pneumonia, with high viral lung loads and extensive virus shedding, but animals only displayed transient mild disease. We determined the infectious dose 50 to be only five infectious particles, making the Syrian hamster a highly susceptible model for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Neither hamster age nor sex had any impact on the severity of disease or course of infection. Finally, prolonged viral persistence in interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain knockout hamsters revealed susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 to adaptive immune control. In conclusion, the Syrian hamster is highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 making it a very suitable infection model for COVID-19 countermeasure development.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Figures

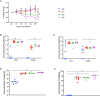

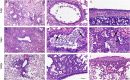
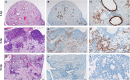
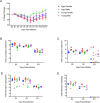
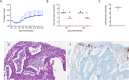
References
-
- CDC COVID Data Tracker 2020 [cited 2020 September 23, 2020]. Maps, Charts and Data]. Available from: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#cases_casesinlast7days.
-
- Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1824–36. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
