The role of IL-22 in intestinal health and disease
- PMID: 32997932
- PMCID: PMC7062536
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20192195
The role of IL-22 in intestinal health and disease
Abstract
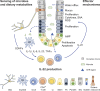
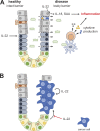
The cytokine interleukin-22 (IL-22) is a critical regulator of epithelial homeostasis. It has been implicated in multiple aspects of epithelial barrier function, including regulation of epithelial cell growth and permeability, production of mucus and antimicrobial proteins (AMPs), and complement production. In this review, we focus specifically on the role of IL-22 in the intestinal epithelium. We summarize recent advances in our understanding of how IL-22 regulates homeostasis and host defense, and we discuss the IL-22 pathway as a therapeutic target in diseases of the intestine, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and cancer.
© 2020 Genentech, a member of the Roche Group
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: Dr. Keir reported "other" from Genentech during the conduct of the study; "other" from Genentech outside the submitted work; and is employed by Genentech. All authors are employees of Genentech. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Aparicio-Domingo P., Romera-Hernandez M., Karrich J.J., Cornelissen F., Papazian N., Lindenbergh-Kortleve D.J., Butler J.A., Boon L., Coles M.C., Samsom J.N., and Cupedo T.. 2015. Type 3 innate lymphoid cells maintain intestinal epithelial stem cells after tissue damage. J. Exp. Med. 212:1783–1791. 10.1084/jem.20150318 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernshtein B., Curato C., Ioannou M., Thaiss C.A., Gross-Vered M., Kolesnikov M., Wang Q., David E., Chappell-Maor L., Harmelin A., et al. 2019. IL-23-producing IL-10Rα-deficient gut macrophages elicit an IL-22-driven proinflammatory epithelial cell response. Sci. Immunol. 4:eaau6571 10.1126/sciimmunol.aau6571 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

