Astaxanthin Inhibits p70 S6 Kinase 1 Activity to Sensitize Insulin Signaling
- PMID: 32998286
- PMCID: PMC7600478
- DOI: 10.3390/md18100495
Astaxanthin Inhibits p70 S6 Kinase 1 Activity to Sensitize Insulin Signaling
Abstract
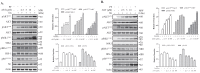
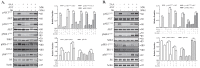
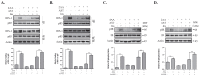
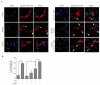
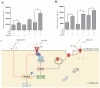
Astaxanthin (AST) is a carotenoid with therapeutic values on hyperglycemia and diabetic complications. The mechanisms of action of AST remain incompletely understood. p70 S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) is a serine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1)S1101 and desensitizes the insulin receptor (IR). Our present study aims to determine if AST improves glucose metabolisms by targeting S6K1. Western blot analysis revealed that AST inhibited the phosphorylation of two S6K1 substrates, S6S235/236 and IRS-1S1101, but enhanced the phosphorylation of AKTT308, AKTS473, and S6K1T389 by feedback activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3 (PI-3) kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6 myotubes. In vitro kinase assays revealed that AST inhibited S6K1 activity with an IC50 value of approximately 13.8 μM. AST increased insulin-induced IR tyrosine phosphorylation and IRS-1 binding to the p85 subunit of PI-3 kinase. Confocal microscopy revealed that AST increased the translocation of the glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane in L6 cells. Glucose uptake assays using a fluorescent dye, 2-NBDG (2-N-(Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino)-2-deoxyglucose), revealed that AST increased glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6 myotubes under insulin resistance conditions. Our study identifies S6K1 as a previously unrecognized molecular target of AST and provides novel insights into the mechanisms of action of AST on IR sensitization.
Keywords: AKT; GLUT4; PI-3 kinase; S6K1; astaxanthin; glucose uptake; insulin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P., Salpea P., Karuranga S., Petersohn I., Malanda B., Gregg E.W., Unwin N., Wild S.H., Williams R. Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20–79 years old adults, 2019 estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020;162:108086. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108086. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9 (th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

