Microvesicle Formation Induced by Oxidative Stress in Human Erythrocytes
- PMID: 32998418
- PMCID: PMC7650597
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9100929
Microvesicle Formation Induced by Oxidative Stress in Human Erythrocytes
Abstract
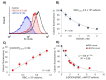
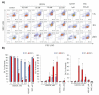
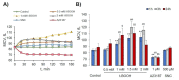
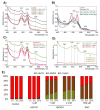
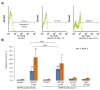
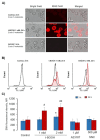
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by different cell types play an important role in many physiological and pathophysiological processes. In physiological conditions, red blood cell (RBC)-derived EVs compose 4-8% of all circulating EVs, and oxidative stress (OS) as a consequence of different pathophysiological conditions significantly increases the amount of circulated RBC-derived EVs. However, the mechanisms of EV formation are not yet fully defined. To analyze OS-induced EV formation and RBC transformations, we used flow cytometry to evaluate cell esterase activity, caspase-3 activity, and band 3 clustering. Band 3 clustering was additionally analyzed by confocal microscopy. Two original laser diffraction-based approaches were used for the analysis of cell deformability and band 3 activity. Hemoglobin species were characterized spectrophotometrically. We showed that cell viability in tert-Butyl hydroperoxide-induced OS directly correlated with oxidant concentration to cell count ratio, and that RBC-derived EVs contained hemoglobin oxidized to hemichrome (HbChr). OS induced caspase-3 activation and band 3 clustering in cells and EVs. Importantly, we showed that OS-induced EV formation is independent of calcium. The presented data indicated that during OS, RBCs eliminated HbChr by vesiculation in order to sacrifice the cell itself, thereby prolonging lifespan and delaying the untimely clearance of in all other respects healthy RBCs.
Keywords: band 3; calcium ionophore A23187; erythrocytes; microparticles; nitric oxide donor; oxidative stress; tert-Bytyl hydroperoxide t-BOOH; vesiculation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Relation Between Extracellular Vesicles Released From Red Blood Cells, Their Cargo, and the Clearance by Macrophages.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 31;13:783260. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.783260. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35432007 Free PMC article.
-
Clearance and phenotype of extracellular vesicles after red blood cell transfusion in a human endotoxemia model.Transfus Apher Sci. 2019 Aug;58(4):508-511. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 Jun 22. Transfus Apher Sci. 2019. PMID: 31253560 Clinical Trial.
-
Phospholipid composition of packed red blood cells and that of extracellular vesicles show a high resemblance and stability during storage.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018 Jan;1863(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.09.012. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018. PMID: 28965917
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Red Blood Cell Concentrates: An Overview.Transfus Med Rev. 2019 Apr;33(2):125-130. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Transfus Med Rev. 2019. PMID: 30910256 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in transfusion-related immunomodulation and the role of blood component manufacturing.Transfus Apher Sci. 2016 Dec;55(3):281-291. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2016.10.018. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Transfus Apher Sci. 2016. PMID: 27865649 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles and lipoproteins - Smart messengers of blood cells in the circulation.J Extracell Biol. 2022 Jul 5;1(7):e49. doi: 10.1002/jex2.49. eCollection 2022 Jul. J Extracell Biol. 2022. PMID: 38938581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Drug Delivery: A Focus on Red Blood Cells-Derived EVs.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 21;15(2):365. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020365. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Characterization of Red Blood Cells Microcirculation under Oxidative Stress.Cells. 2021 Dec 16;10(12):3552. doi: 10.3390/cells10123552. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944060 Free PMC article.
-
Aging Injury Impairs Structural Properties and Cell Signaling in Human Red Blood Cells; Açaì Berry Is a Keystone.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 1;12(4):848. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107223 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis, Membrane Trafficking, Functions, and Next Generation Nanotherapeutics Medicine of Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 May 18;16:3357-3383. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S310357. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34040369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

