Characteristics and Clinical Outcome of Breast Cancer Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases
- PMID: 32998430
- PMCID: PMC7600746
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12102787
Characteristics and Clinical Outcome of Breast Cancer Patients with Asymptomatic Brain Metastases
Abstract
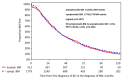
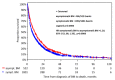
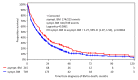
Background: Brain metastases (BM) have become a major challenge in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Methods: The aim of this analysis was to characterize patients with asymptomatic BM (n = 580) in the overall cohort of 2589 patients with BM from our Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer Network Germany (BMBC) registry. Results: Compared to symptomatic patients, asymptomatic patients were slightly younger at diagnosis (median age: 55.5 vs. 57.0 years, p = 0.01), had a better performance status at diagnosis (Karnofsky index 80-100%: 68.4% vs. 57%, p < 0.001), a lower number of BM (>1 BM: 56% vs. 70%, p = 0.027), and a slightly smaller diameter of BM (median: 1.5 vs. 2.2 cm, p < 0.001). Asymptomatic patients were more likely to have extracranial metastases (86.7% vs. 81.5%, p = 0.003) but were less likely to have leptomeningeal metastasis (6.3% vs. 10.9%, p < 0.001). Asymptomatic patients underwent less intensive BM therapy but had a longer median overall survival (statistically significant for a cohort of HER2-positive patients) compared to symptomatic patients (10.4 vs. 6.9 months, p < 0.001). Conclusions: These analyses show a trend that asymptomatic patients have less severe metastatic brain disease and despite less intensive local BM therapy still have a better outcome (statistically significant for a cohort of HER2-positive patients) than patients who present with symptomatic BM, although a lead time bias of the earlier diagnosis cannot be ruled out. Our analysis is of clinical relevance in the context of potential trials examining the benefit of early detection and treatment of BM.
Keywords: asymptomatic; brain metastases; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
V.M. (Volkmar Müller) received speaker honoraria from Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Pfizer, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Teva, Seattle Genetics and consultancy honoraria from Genomic Health, Hexal, Roche, Pierre Fabre, Amgen, ClinSol, Novartis, MSD, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Lilly, Tesaro, Seattle Genetics and Nektar. Institutional research support from Novartis, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Genentech. Travel grants: Roche, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo. M.T. is a member of advisory Board of Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Exact Sciences, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, onkowissen.de, Pfizer, Pierre-Fabre, Roche, he provides manuscript support for Amgen, Celgene, Roche, received travel reimbursement from Amgen, Art Tempi, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Connect Medica, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Exact Sciences, Hexal, I-Med-Institute, Lilly, MCI, MSD, Novartis, Omniamed, Pfizer, Roche, congress support from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Daiichi Sanyko, Hexal, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche. M.T. is involved in lecture by Amgen, Art Tempi, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Connect Medica, Eisai, Exact Sciences, Hexal, I-Med-Institute, Lilly, MCI, MSD, Novartis, onkowissen.de, Omniamed, Pfizer, Roche, Vifor. M.T. received trial funding by Exact Sciences. M.S. received honoraria for speaker or consultancy role from AMGEN, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Lilly, Myelo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, Roche and Seattle Genetics. He received research funding from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Eisai, Genentech, German Breast Group, Myelo Therapeutics, Novartis, Palleos, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pierre-Fabre, and Roche. He received travel reimbursement from Pfizer and Roche. P.F. reports personal fees from Novartis, Roche, Pfizer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Astra Zeneca, Eisai, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Pierre Fabre, Seattle, grants from Biontech, Cepheid, Genetics, during the conduct of the study. V. Möbus received speaker honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Roche, Teva and consultancy honoraria from Roche, Amgen, Tesaro and Myelo Therapuetics. C.D. has stock and other ownership interests by Sividon Diagnostics (now Myriad), recieved honoraria by Novartis and Roche, has consulting or advisory role by MSD Oncology and Daiichi Sankyom, has patents, royalties or other intellectual property by VMScope digital pathology software, has two patents (patent application: EP18209672—cancer immunotherapy, patent application EP20150702464 - therapy response), received travel, accommodations, expenses from Roche, his institution received research funding by Myriad Genetics. S.L. has no conflict of interests concerning the presented analysis. S.L. has following relevant financial activities outside the submitted work (with conflict of interests): grants and honorario for lectures and ad boards paid to institute from Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche; honorario for lectures and ad boards paid to institute from Seattle Genetics, Samsung, PriME/Medscape; personal fees for lecture from Chugai; grants from Teva, Vifor; grant and honorarium paid to institute from Daiichi-Sankyo; honorarium for ad boards paid to institute from Lilly; advisor honorarium paid to institute from Eirgenix, BMS, Puma; honorarium paid for institute from MSD, grant paid to institute from Immunomedics; grant and honorarium for lectures and ad boards paid to institute from Astra Zeneca. S.L. has intellectual property broadly relevant to the work (pending patent EP14153692.0 Immunsignature in TNBC). IW has no conflict of interest concerning the presented analysis, she received speaker‘s honoraria outside this work from Amgen, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre Pharme, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term survival of breast cancer patients with brain metastases: subanalysis of the BMBC registry.ESMO Open. 2023 Jun;8(3):101213. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101213. Epub 2023 Apr 17. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 37075697 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer with brain metastases and establishment of a prognostic model: a 10-year, single-center, real-world study of 559 cases.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Aug;9(16):1331. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3734. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34532468 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Prognostic Factors for Patients With HER2-overexpressing Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases in the Era of HER2-targeted Therapy: An Argument for Earlier Detection.Clin Breast Cancer. 2018 Oct;18(5):353-361. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29337140
-
Radiation therapy for brain metastases in breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer. 2011 Oct;18(4):244-51. doi: 10.1007/s12282-010-0207-8. Epub 2010 May 11. Breast Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20458564 Review.
-
Systemic Treatment Options for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases beyond Trastuzumab: A Literature Review.Breast Care (Basel). 2017 Jul;12(3):168-171. doi: 10.1159/000467387. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Breast Care (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28785185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of breast cancer brain metastasis.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov 24;14(11):445-458. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i11.445. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38059189 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of patients with brain metastases from human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: subanalysis of Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer Registry.ESMO Open. 2022 Jun;7(3):100495. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100495. Epub 2022 May 30. ESMO Open. 2022. PMID: 35653983 Free PMC article.
-
Association between age and the presence and mortality of breast cancer synchronous brain metastases in the United States: A neglected SEER analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 23;10:1000415. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1000415. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36211679 Free PMC article.
-
Symptoms of Isolated Optic Neuropathy in a Patient with Systemic, Brain, and Meningeal Metastases from Breast Cancer: A Case Report.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024 Jan 29;15(1):71-77. doi: 10.1159/000536189. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38288028 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of the management of brain metastases from hormone receptor positive breast cancer.J Neurooncol. 2023 Mar;162(1):45-57. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04276-9. Epub 2023 Mar 8. J Neurooncol. 2023. PMID: 36884200 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

