Development and Optimization of In-house ELISA for Detection of Human IgG Antibody to SARS-CoV-2 Full Length Spike Protein
- PMID: 32998438
- PMCID: PMC7601663
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9100803
Development and Optimization of In-house ELISA for Detection of Human IgG Antibody to SARS-CoV-2 Full Length Spike Protein
Abstract
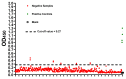
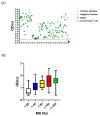
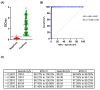
The ongoing coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), poses a threat to human health. Despite this, many affected countries are now in the process of gradual lifting of COVID-19 restrictions that were initially implemented in response to the pandemic. The success of the so-called "exit strategy" requires continued surveillance of virus circulation in the community and evaluation of the prevalence of protective immunity among population. Serology tests are valuable tools for these purposes. Herein, SARS-CoV-2 full-length spike (S) recombinant protein was utilized to develop and optimize an indirect enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) that enables a reliable detection of virus-specific IgG antibody in human sera. Importantly, the performance of this assay was evaluated utilizing micro-neutralization (MN) assay as a reference test. Our developed ELISA offers 100% sensitivity, 98.4% specificity, 98.8% agreement, and high overall accuracy. Moreover, the optical density (OD) values of positive samples significantly correlated with their MN titers. The assay specifically detects human IgG antibodies directed against SARS-CoV-2, but not those to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) or human coronavirus HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1). The availability of this in-house ELISA protocol would be valuable for various diagnostic and epidemiological applications.
Keywords: COVID-19; ELISA; SARS-CoV-2; immunoassay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General’s Remarks at the Media Briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. [(accessed on 11 April 2020)];2020 Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at....
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020. [(accessed on 11 April 2020)];2020 Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
-
- Chan K.W., Wong V.T., Tang S.C.W. COVID-19: An Update on the Epidemiological, Clinical, Preventive and Therapeutic Evidence and Guidelines of Integrative Chinese-Western Medicine for the Management of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020;48:737–762. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500378. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

