Effects of Ketamine on Rodent Fear Memory
- PMID: 32998470
- PMCID: PMC7582895
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197173
Effects of Ketamine on Rodent Fear Memory
Abstract
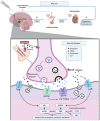
Ketamine, a multimodal anesthetic drug, has become increasingly popular in the treatment of pain following traumatic injury as well as treatment-resistant major depressive disorders. However, the psychological impact of this dissociative medication on the development of stress-related disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) remains controversial. To address these concerns, preclinical studies have investigated the effects of ketamine administration on fear memory and stress-related behaviors in laboratory animals. Despite a well-documented line of research examining the effects of ketamine on fear memory, there is a lack of literature reviews on this important topic. Therefore, this review article summarizes the current preclinical literature on ketamine and fear memory with a particular emphasis on the route, dose, and timing of ketamine administration in rodent fear conditioning studies. Additionally, this review describes the molecular mechanisms by which ketamine may impact fear memory and stress-related behaviors. Overall, findings from previous studies are inconsistent in that fear memory may be increased, decreased, or unaltered following ketamine administration in rodents. These conflicting results can be explained by factors such as the route, dose, and timing of ketamine administration; the interaction between ketamine and stress; and individual variability in the rodent response to ketamine. This review also recommends that future preclinical studies utilize a clinically relevant route of administration and account for biological sex differences to improve translation between preclinical and clinical investigations.
Keywords: PTSD; fear conditioning; fear memory; intravenous; ketamine; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of ketamine on fear memory extinction: a review of preclinical literature.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 30;19:1546460. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1546460. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40370666 Free PMC article.
-
Association between intravenous ketamine-induced stress hormone levels and long-term fear memory renewal in Sprague-Dawley rats.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112259. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112259. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31560919
-
Enhanced fear memories and brain glucose metabolism (18F-FDG-PET) following sub-anesthetic intravenous ketamine infusion in Sprague-Dawley rats.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Nov 30;8(1):263. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0310-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30504810 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine reverses the impaired fear memory extinction and accompanied depressive-like behaviors in adolescent mice.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Feb 3;379:112342. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112342. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31705920
-
The emergence of ketamine as a novel treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder.Adv Pharmacol. 2020;89:261-286. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Adv Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32616209 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Ketamine Facilitates Fear Memory Extinction in a Rat Model of PTSD Along With Restoring Glutamatergic Alterations and Dendritic Atrophy in the Prefrontal Cortex.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 17;13:759626. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.759626. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370690 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Fear Memories and Altered Brain Glucose Metabolism (18F-FDG-PET) following Subanesthetic Intravenous Ketamine Infusion in Female Sprague-Dawley Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 8;23(3):1922. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031922. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163844 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine Reduces Avoidance Responses During Re-Exposition to Aversive Stimulus: Comparison Between (S)-Isomer and Racemic Mixture.Brain Sci. 2024 Dec 22;14(12):1291. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121291. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766490 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mGluR5 on the therapeutic effects of ketamine in Wistar rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Jul;241(7):1399-1415. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06571-3. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38459971 Free PMC article.
-
Herniarin, Dimethylfraxetin and Extracts from Tagetes lucida, in Psychosis Secondary to Ketamine and Its Interaction with Haloperidol.Plants (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;11(20):2789. doi: 10.3390/plants11202789. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saur L., Neves L.T., Greggio S., Venturin G.T., Jeckel C.M.M., Costa Da Costa J., Bertoldi K., Schallenberger B., Siqueira I.R., Mestriner R.G., et al. Ketamine promotes increased freezing behavior in rats with experimental PTSD without changing brain glucose metabolism or BDNF. Neurosci. Lett. 2017;658:6–11. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

