Groundwater Arsenic Distribution in India by Machine Learning Geospatial Modeling
- PMID: 32998478
- PMCID: PMC7579008
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17197119
Groundwater Arsenic Distribution in India by Machine Learning Geospatial Modeling
Abstract
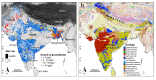
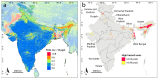
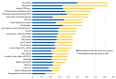
Groundwater is a critical resource in India for the supply of drinking water and for irrigation. Its usage is limited not only by its quantity but also by its quality. Among the most important contaminants of groundwater in India is arsenic, which naturally accumulates in some aquifers. In this study we create a random forest model with over 145,000 arsenic concentration measurements and over two dozen predictor variables of surface environmental parameters to produce hazard and exposure maps of the areas and populations potentially exposed to high arsenic concentrations (>10 µg/L) in groundwater. Statistical relationships found between the predictor variables and arsenic measurements are broadly consistent with major geochemical processes known to mobilize arsenic in aquifers. In addition to known high arsenic areas, such as along the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, we have identified several other areas around the country that have hitherto not been identified as potential arsenic hotspots. Based on recent reported rates of household groundwater use for rural and urban areas, we estimate that between about 18-30 million people in India are currently at risk of high exposure to arsenic through their drinking water supply. The hazard models here can be used to inform prioritization of groundwater quality testing and environmental public health tracking programs.
Keywords: India; arsenic; geospatial modeling; groundwater; machine learning; random forest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Famiglietti J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014;4:945–948. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2425. - DOI
-
- Polya D.A., Middleton D.R. Arsenic in drinking water: Sources & human exposure. In: Bhattacharya P., Polya D.A., Draganovic D., editors. Best Practice Guide on the Control of Arsenic in Drinking Water. 1st ed. International Water Association Publishing; London, UK: 2017. Chapter 1.
-
- Smedley P., Kinniburgh D. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002;17:517–568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5. - DOI
-
- Charlet L., Polya D.A. Arsenic in shallow, reducing groundwaters in southern Asia: An environmental health disaster. Elements. 2006;2:91–96. doi: 10.2113/gselements.2.2.91. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

